Figure 5.
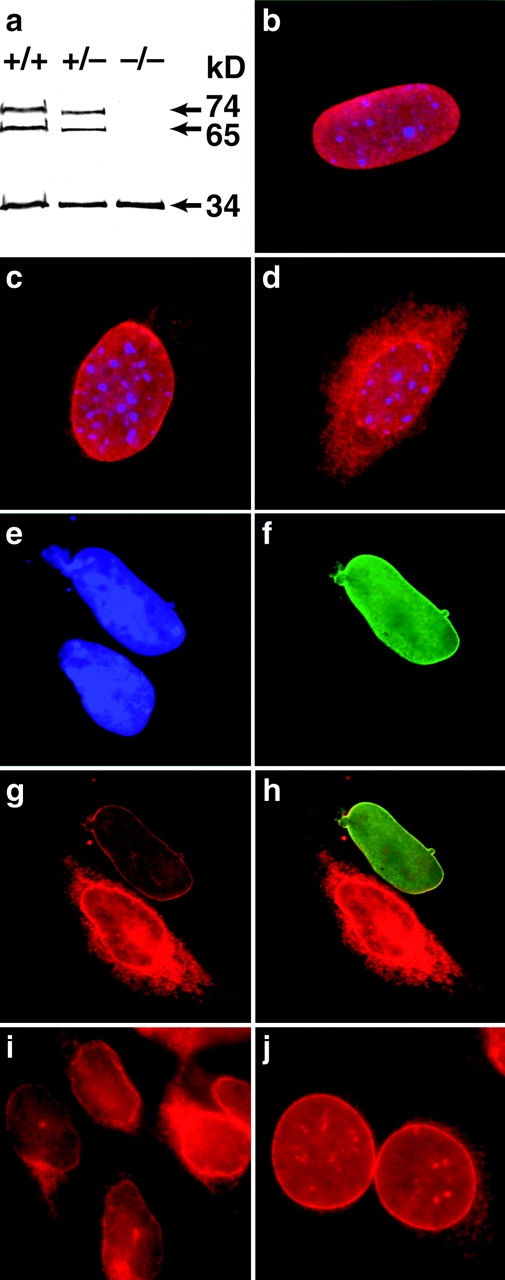
(a) Western blot analysis of emerin (34 kD) and lamins A and C (74 and 65 kD, respectively) in +/+, +/−, and −/− Lmna MEFs showing no difference in emerin levels between different genotypes. (b) In wild-type cells, emerin is localized exclusively to the nuclear envelope. (c) In the heterozygotes, some emerin localization can be detected in the cytoplasm. (d) In the lamin A/C −/− cells, emerin is largely cytoplasmic although some localization to the nuclear envelope is still apparent. Expression of human lamin A in Lmna null MEFs results in relocalization of emerin to the nuclear envelope. (e) DAPI staining revealing the nuclei of two MEFs. (f) The upper MEF expresses human lamin A localized exclusively to the nuclear envelope. (g) Both cells express emerin but in the lamin A null cell, emerin is localized predominantly in the cytoplasmic compartment, whereas in the lamin A positive MEF, emerin is localized almost entirely to the nuclear envelope. (h) Merged image showing colocalization of emerin and human lamin A in the nuclear envelope. (i and j) Emerin distribution in P19EC cells (i) and (j) their differentiated derivatives P19MES that express A-type lamins. Both cell types exhibit NE-associated emerin.
