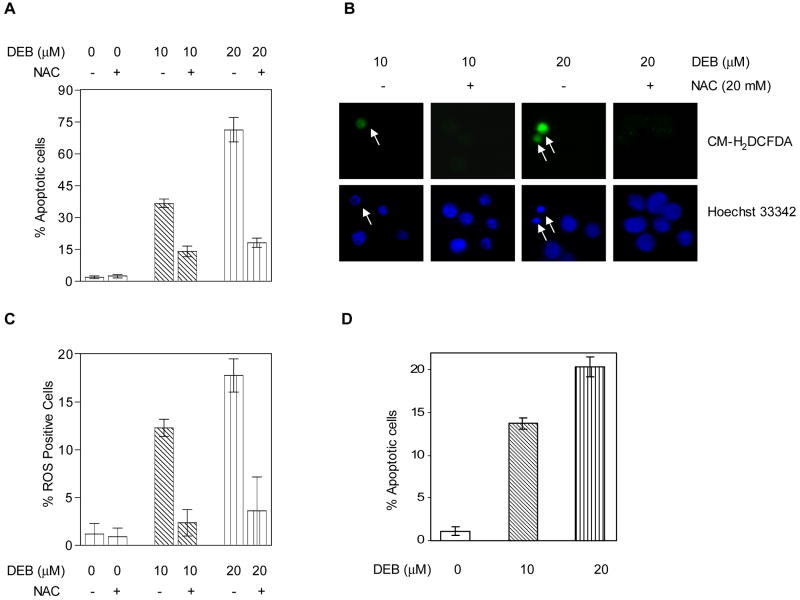
Figure 7. DEB-induced apoptosis is mediated through DEB-induced reactive oxygen species.
TK6 cells were exposed to DEB as indicated, in the presence or absence of the ROS scavenger N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC), and apoptosis or ROS were quantitated, as described in Methods. A. Effect of NAC on DEB-induced apoptosis at 24 h post-exposure. B. Representative fluorescence microscopy pictures demonstrating the induction of ROS only in cells undergoing DEB-induced apoptosis and the effect of NAC on ROS and apoptosis. Hoechst 33342 was used to stain nuclei in order to identify apoptotic cells as well as total number of cells. CM-H2DCFDA (5-(and 6)-chloromethyl-2’,7’-dichlorodihyrofluoroscein diacetate) was utilized as the probe for the detection of ROS-positive cells. C. Effect of NAC on the DEB-induced generation of ROS at 12 h post-exposure to DEB, expressed as a percentage of ROS positive cells. D. The effect of DEB on the percentage of apoptotic cells at 12 h post-DEB exposure.