FIG. 1.
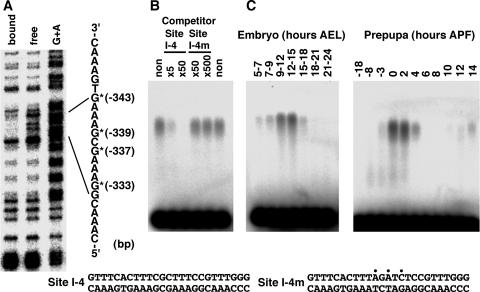
Determination of the binding site and developmental expression pattern of factor I-4. (A) Methylation interference using a 400-bp Eco52I-HincII fragment. Positions of nucleotides showing methylation interference are represented by asterisks with the distance from the transcription start site. The G+A Maxam-Gilbert sequencing reaction was used as a marker. (B) Confirmation of sequence-specific binding to the identified site by a gel mobility shift competition assay. 32P-labeled site I-4 DNA was used as a probe, and the indicated amounts of site I-4 or site I-4m competitor DNA compared with the probed site I-4 DNA were added to the binding reaction mixtures. The nucleotide sequences of site I-4 and site I-4m DNAs are indicated at the bottom. Positions of introduced mutations are indicated by dots. (C) Confirmation of factor I-4 binding by gel mobility shift assays using developmentally staged nuclear extracts at embryonic stages (left) and at the onset of metamorphosis (right). 32P-labeled site I-4 DNA was used as a probe. AEL, after egg laying.