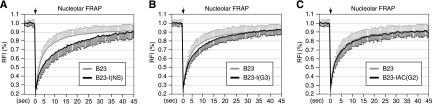
FIG. 5.
The NpLS activity of the I domain of NS and, to a lesser extent, GNL3L, is mediated by a nucleoplasmic retention mechanism. The exchange rates between the nucleolus and the nucleoplasm of the B23 and B23-NpLS domain fusion proteins were measured by the nucleolar FRAP paradigm described in the legend to Fig. 1E. (A) The FRAP recovery rate of the NS I domain fused to the B23 protein [B23-I(NS)] is significantly delayed compared to the recovery rate of the control B23 protein. (B) The FRAP recovery rate of the GNL3L I domain fused to the B23 protein shows a slight but statistically significant decrease at the 5-, 10-, and 15-s time points compared to the recovery rate of the control B23 protein (P < 0.005; n = 50). (C) The FRAP recovery rates of the Ngp1 IAC domain fused to the B23 protein and the control B23 protein are identical. Error bars showing standard deviations are omitted on one side of the curves for clarity.