FIG. 6.
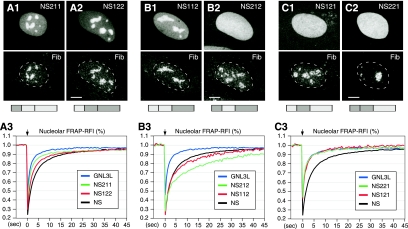
The B-C domains can be exchanged between NS and GNL3L and still maintain their relative activities, but the ability of the G domain to regulate the NpLS activity is protein specific. Chimeric proteins of NS and GNL3L were created that cross over at the highly conserved G5* and G1 motifs (see Fig. S4 in the supplemental material for details). Protein distribution was detected by using a C-terminally fused GFP and counterstained with antifibrillarin (Fib) antibody. When only the B-C domains are switched, the chimeric proteins NS211 (A1) and NS122 (A2) maintain their nucleolar distribution, and their FRAP recovery rates fall between those of NS and GNL3L (A3). When the G domain of NS is fused to the NpLS domain of GNL3L, the chimeric protein appears nucleolar (B1; NS112) or diffuse (B2; NS212), depending on which B-C domain it is coupled to. The FRAP recovery rates of these two mutants are as slow as or slower than that of NS (B3). When the G domain of GNL3L is fused to the NpLS domain of NS, the chimeric proteins are diffusely localized in the nucleus (C1 and C2), and their protein exchange rates are as fast as that of GNL3L (C3). The chimeric protein structures are depicted below the panels, with light and dark grey boxes representing protein origin from NS or GNL3L, respectively.