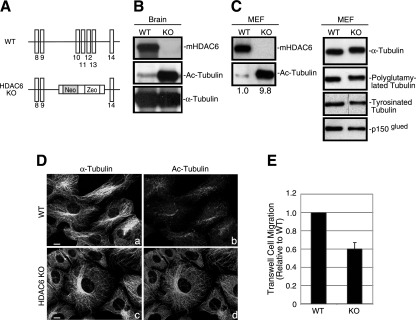
FIG. 1.
Accumulation of hyperacetylated microtubules in HDAC6 KO tissues and MEFs. (A) A schematic diagram of the targeting strategy with mouse HDAC6 genomic sequences. Exons (vertical bars) 10 to 13 were replaced by a targeting vector containing a neomycin (Neo) and zeocin (Zeo) cassette, resulting in the disruption of the first catalytic domain of HDAC6. The sequences are not drawn to scale. (B and C) Immunoblotting analysis of brain samples (B) or MEFs (C) from wild-type (WT) or HDAC6 KO mice revealed the absence of HDAC6 protein and significantly elevated tubulin acetylation in HDAC6 KO animals. The relative amount of acetylated α-tubulin (Ac-Tubulin) is provided under panel C. p150glued was shown as a loading control. (D) Wild-type (a and b) and HDAC6 KO (c and d) MEFs were immunostained with antibodies for acetylated α-tubulin (b and d) and α-tubulin (a and c). Note that almost the entire microtubule network in HDAC6 KO MEFs was stained positive for acetylated α-tubulin. Bar = 10 μm. (E) Cell motility of wild-type and KO MEFs was analyzed by Boyden chamber cell migration assays. Average values with standard errors of the means from four independent experiments are shown.