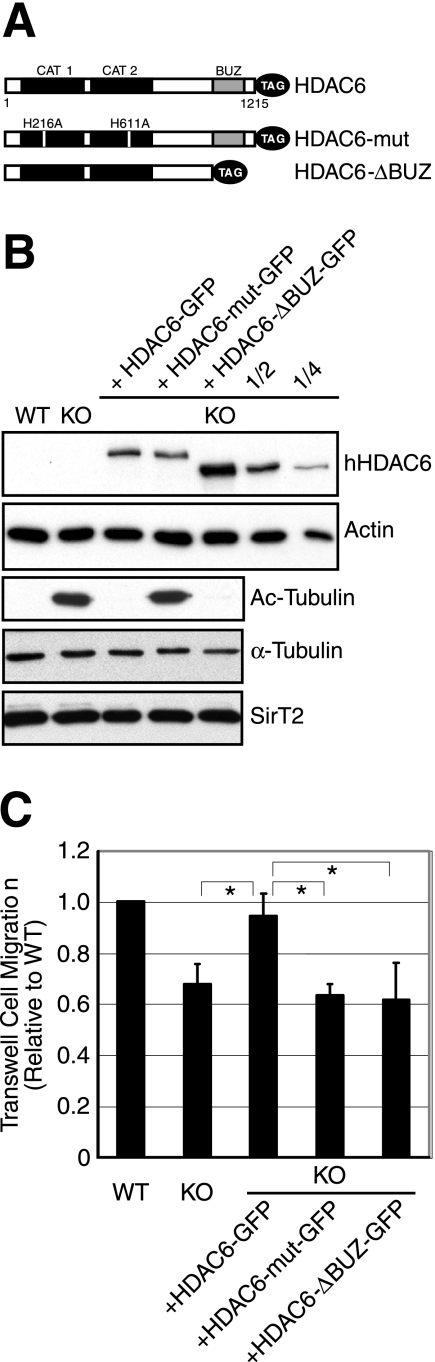
FIG. 2.
Both enzymatic activity and the BUZ domain of HDAC6 are required to rescue motility defects of HDAC6 KO cells. (A) Schematic representation of the human HDAC6 constructs used in this study. The constructs are tagged either with GFP or with FLAG. Boxes in black, catalytic domains; boxes in gray, BUZ domain. H216A and H611A are histidine-to-alanine point mutations that inactivate the deacetylase activity of HDAC6. (B) Wild-type, HDAC6 KO, and HDAC6 KO MEFs stably expressing the human HDAC6 constructs were analyzed for the level of HDAC6 in the cells using an anti-human HDAC6 antibody (upper panel). In addition, the HDAC6-ΔBUZ-GFP sample was also serially diluted by two- and fourfold for analysis. Total and acetylated α-tubulin and SirT2 levels were examined using corresponding antibodies. (C) Quantification of cell migration using Boyden chamber assays for cell lines described for panel B. Each bar represents an average value plus standard error of the mean from four independent experiments. *, t < 0.05 in two-tailed and paired t test.