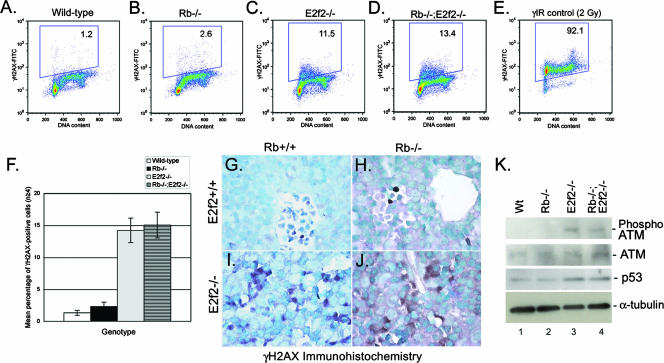
FIG. 9.
E2f-2 loss induces DNA double-strand breaks in wild-type and Rb null erythroblasts. (A to D) Flow cytometric analysis of intracellular staining for γH2AX on E13.5 erythroblasts derived from wild-type (A), Rb−/− (B), E2f2−/− (C), or Rb−/−; E2f2−/− (D) fetal liver and differentiated in culture for 18 h. (E) Control staining for γH2AX at 1 h after gamma irradiation of wild-type erythroblasts. (F) Quantitative analysis of the effect Rb loss and E2f-2 loss had on the incidence of DNA double-strand breaks. Data are shown as the mean percentage of γH2AX-positive cells for at least four different samples per genotype, and error bars represent the SD from the mean. (G to J) Immunohistochemical staining for γH2AX on sections of E13.5 wild-type (G), Rb−/− (H), E2f2−/− (I), and Rb−/−; E2f2−/− (J) fetal livers. (K) Western blotting analysis of phospho-ATM (ser1981), ATM, and p53 levels in wild-type (Wt), Rb−/−, E2f2−/−, and Rb−/−; E2f2−/− E13.5 fetal liver extracts. Protein loading was controlled for by α-tubulin. FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate.