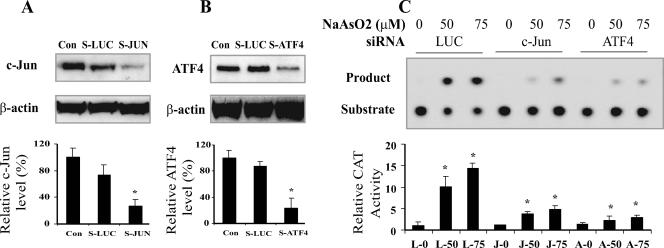
FIG. 5.
ATF4-deficient or c-Jun-deficient 10T½ cells are defective for arsenite-induced mAPE1 promoter activation. (A and B) Down-regulation of c-Jun (A) and ATF4 (B) proteins by siRNA (indicated by S-JUN and S-ATF4, respectively, with S-LUC as the control). Cells were infected with retrovirus producing the indicated siRNA, and puromycin-resistant cells were expanded (for 7 or 8 days for S-ATF4 and 10 to 12 days for S-JUN) for treatment and analysis. Cell-free lysates were generated for protein analysis by immunoblotting. Con, control with no siRNA treatment. (C) Defective mAPE1 response to sodium arsenite in c-Jun-deficient or ATF4-deficient cells. Following treatment as shown in panels A and B to suppress c-Jun or ATF4 expression, cells were treated with the indicated concentration of sodium arsenite for 30 min, followed by a 6-h incubation in arsenite-free medium before harvesting and assay. CAT reporter assays were carried out as described in the legend to Fig. 2. The data shown are based on at least three independent experiments. Standard deviations are indicated by error bars. Values that were significantly different (P < 0.0) from the value for the control are indicated by an asterisk. The designations below the bars indicate the siRNA and arsenite treatments (e.g., L-0 corresponds to LUC siRNA and no arsenite, J-50 corresponds to c-JUN siRNA and 50 μM arsenite treatment, and A-0 corresponds to ATF4 siRNA and no arsenite).