Figure 1.
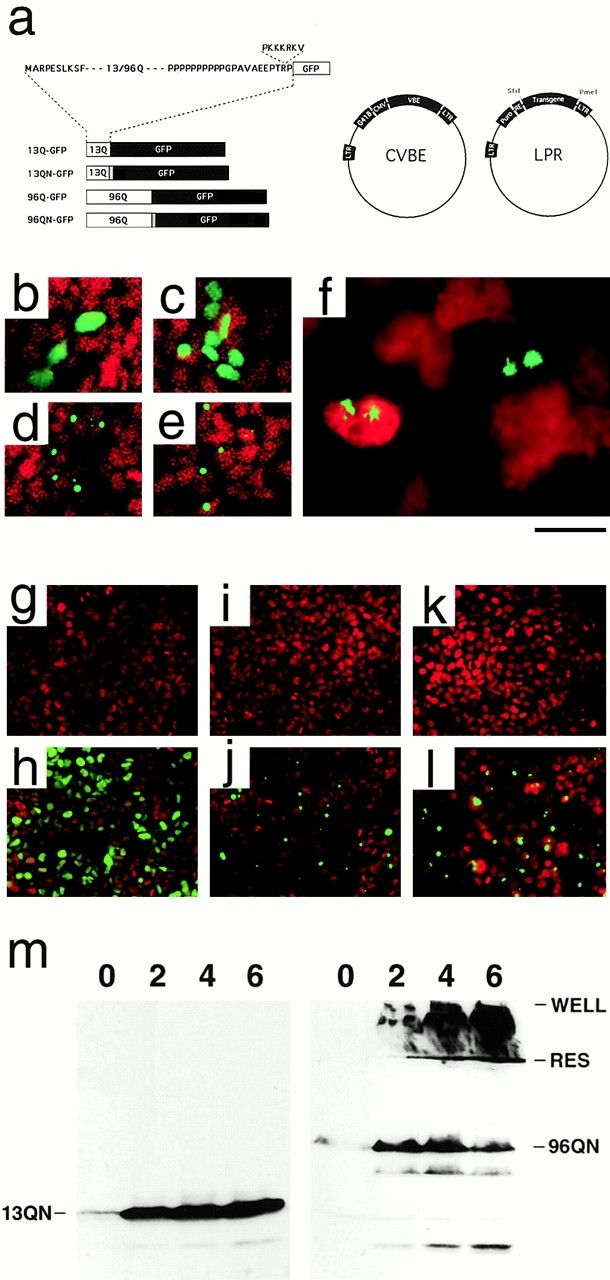
PolyQ–GFP reporter constructs transiently and regulatably expressed in HEK293 cells. (a, left) Schematic of polyQ–GFP fusion proteins indicating Htt exon I–derived sequences (white), SV 40 NLS (gray), and eGFP sequences (black). (a, right) Schematic of CVBE and LPR Moloney murine leukemia virus–based retroviral vectors used in production of inducible polyQ cell lines. CVBE encodes flanking long terminal repeats (LTRs), a G418-resistance gene (G418), the immediate–early CMV promoter (CMV), and the VBE transactivator protein (VBE). LPR encodes long term repeats, a puromycin-resistance gene (Puro), a minimal CMV promoter with six tandem ecdysone response elements (RE), and a SfiI–PmeI polylinker for insertion of the polyQ transgenes. (b–f) Propidium iodide nuclear-stained (red) HEK293 cells transiently transfected with the expression construct 13Q–GFP (b), 13QN–GFP (c), 96Q–GFP (d), and 96QN–GFP (e). GFP produces the bright green fluorescence. (f) IAs in transfected cells revealing stellate fibrous appearance of IAs at high magnification. 72-h vehicle- (g) or ligand-treated (h) 13QN cells stained with the nuclear stain DAPI (red), vehicle- (i) or ligand-treated (j) 96Q cells, and vehicle- (k) or ligand-treated (l) 96QN cells. Bright GFP-positive profiles indicate IA formation. (m) Western blot analysis of induced 13QN (left) or 96QN (right) cells. Numbers at the top of each blot indicate the number of days of induction. WELL, bottom of the well; RES, bottom of the stacking gel and the beginning of the resolving gel. Bar: (b–e) 125 μm; (f) 20 μm; (g–l) 250 μm.
