Figure 5.
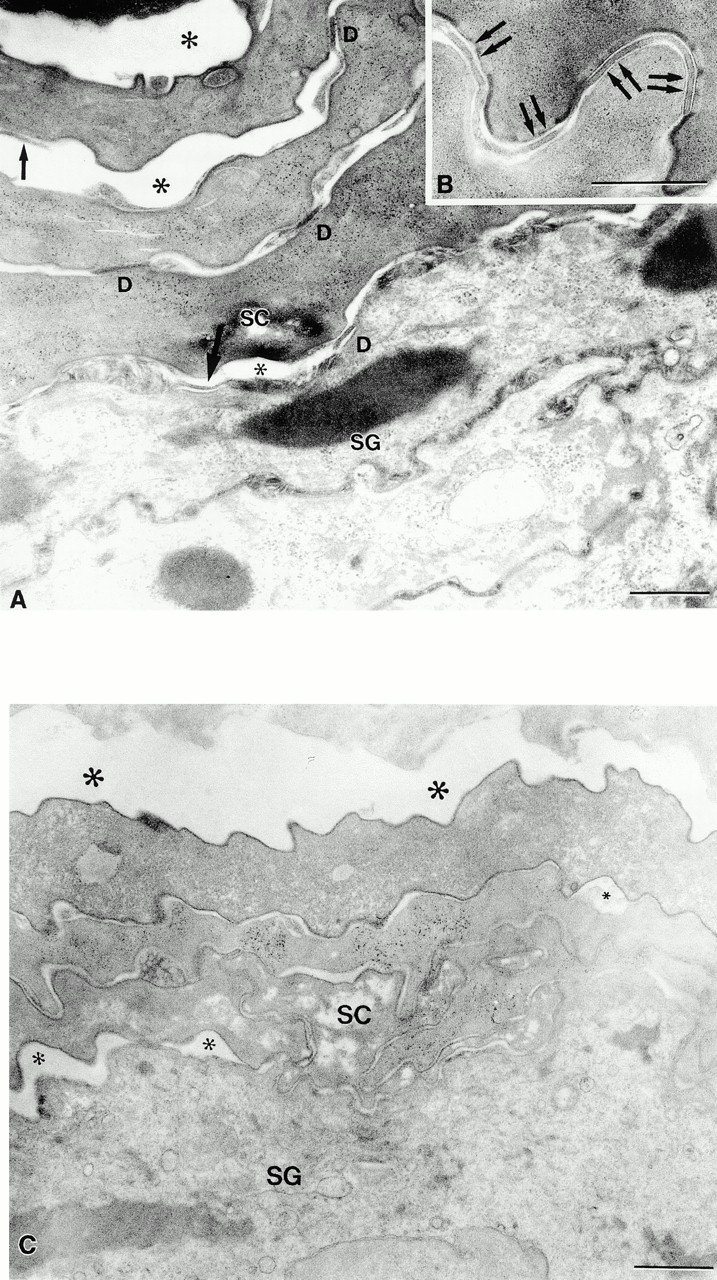
Dsg 3 in the superficial epidermis of transgenic mice results in premature dissolution of desmosomes and cleft formation in the stratum corneum. (A) Dissolution of desmosomes begins at the stratum granulosum (SG)–stratum corneum (SC) interface. Desmosomal detachment (single arrows) results in cleft formation (*) at all levels of the stratum corneum. D, normal-appearing desmosomes. (B) Normal-appearing desmosomes in control stratum corneum. (C) Normal mucous membrane (lip) also reveals early cleft formation. Note small (small *) clefts at SG–SC interface and larger clefts (large *) at higher levels. Bar: 0.5 μm (A and B), 1 μm (C). Osmium tetroxide postfixation.
