Figure 5.
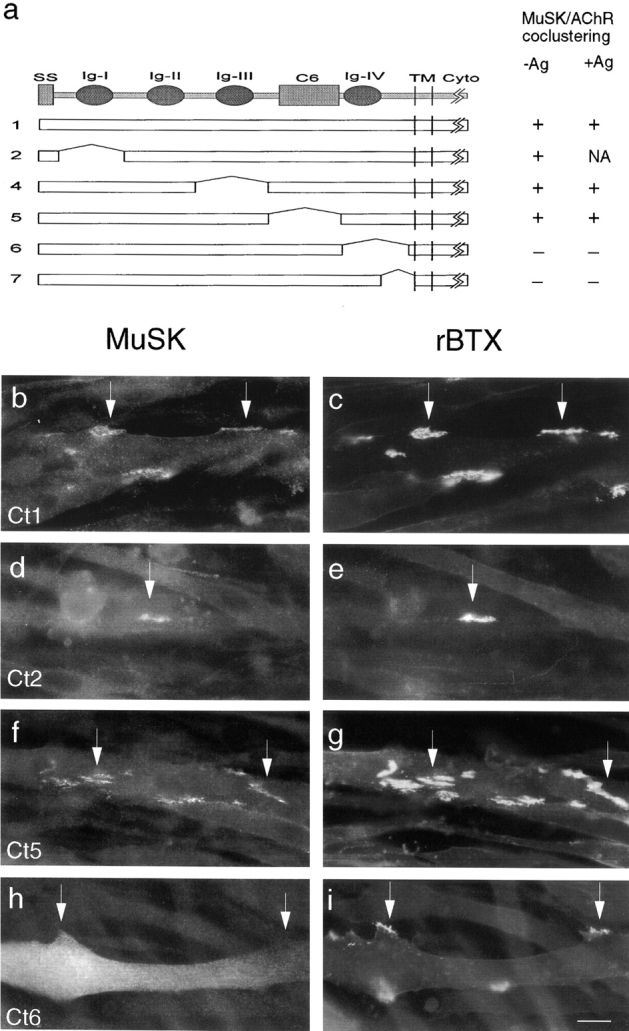
Carboxy-terminal regions of the MuSK ectodomain are required for association with AChR clusters in myotubes. (a) MuSK constructs, numbered as in Fig. 2, which were tested for their ability to associate with AChR clusters in MuSK −/− muscle cells. To the right of each construct is indicated whether it was concentrated at spontaneous or agrin-induced clusters. NA, not applicable, because agrin did not induce AChR clusters in these cells. (b–i) MuSK and AChR localization in cells transfected with expression vectors encoding MuSK constructs that colocalize (b and c, construct 1; d and e, construct 2; f and g, construct 5) or do not colocalize (h and i, construct 6) with AChRs. Cells were treated with agrin for 18 h, and then doubly stained with anti-mouse MuSK antibodies (b, d, f, and h) and rBTX (c, e, g, and i). Arrows indicate corresponding points in the two images of each field. Bar, 20 μm.
