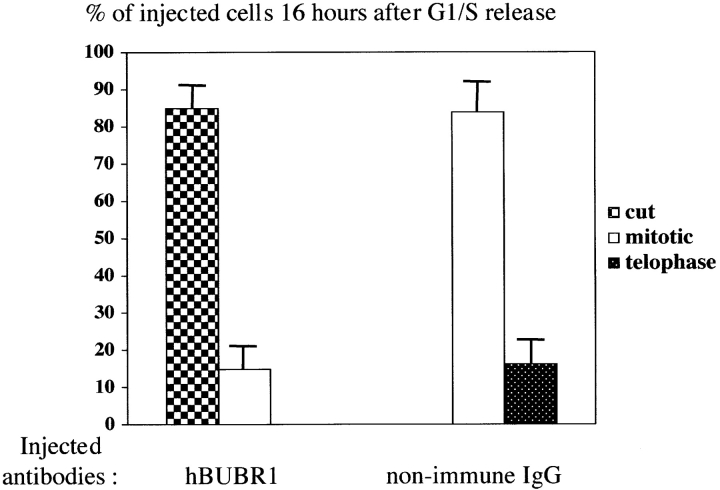
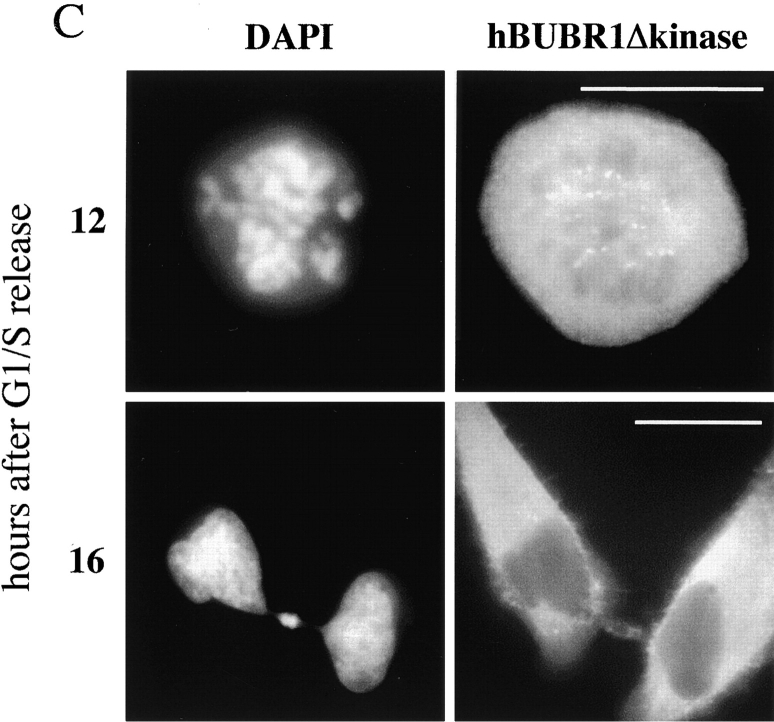
Figure 3.
hBUBR1 is essential for cells to proceed normally through mitosis. (A) Synchronized Hela cells released from the G1/S boundary were injected with nonimmune or hBUBR1 antibodies and sampled at 12 or 16 h later. (rows 1–3) 12 h after release from the G1/S boundary, injected cells entered mitosis. (row 1) Metaphase cell injected with nonimmune IgG (middle) stained for endogenous hBUBR1 (right). (rows 2 and 3) Prometaphase and anaphase cells injected with hBUBR1 antibodies (middle) and stained for CENP-E (right). (row 4) 16 h after release from the G1/S boundary, hBUBR1 injected cells (middle) divided with lagging chromosomes trapped in the cleavage furrow. Centromeres (arrowheads) stained with ACA and visualized with Texas red anti-human secondary antibodies. Insets in rows 3 and 4 are longer exposures and enlargements of boxed areas. Injected antibodies were visualized with Cy5 anti-rabbit secondary antibody (middle). Endogenous hBUBR1 was stained with rat anti–hBUBR1 and detected with Cy2 anti-rat (row 1, right). CENP-E was stained with mouse monoclonal anti-CENP-E (mAb177) and detected with Cy2 anti-mouse secondary antibodies (rows 2 and 3, right). Chromosomes and nuclei were stained with DAPI (left). (B) 16 h after release from the G1/S boundary, nonimmune IgG– and hBUBR1 antibody–injected cells were scored for mitotic (open bar), normal telophase (dotted bar) or aberrantly divided cut (checkered bar) based on a combination of DAPI staining and phase-contrast images. Histogram compares relative percentages of each of the three phenotypes. The plotted values are the means plus SD from at least three experiments. (C) Cells expressing gfp:hBUBR1Δkinase exit mitosis with prematurely. Synchronized Hela cells transfected with gfp:hBUBR1Δkinase enter mitosis (top row) 12 h after release from the G1/S boundary. By 16 h, most cells expressing the kinase mutant produced cells that divided with lagging chromosomes trapped in the cleavage furrow (bottom). Bars, 10 μm.