FIGURE 8. Mass spectrometric detection of endogenous nitroalkylated GAPDH in red blood cells obtained from healthy humans.
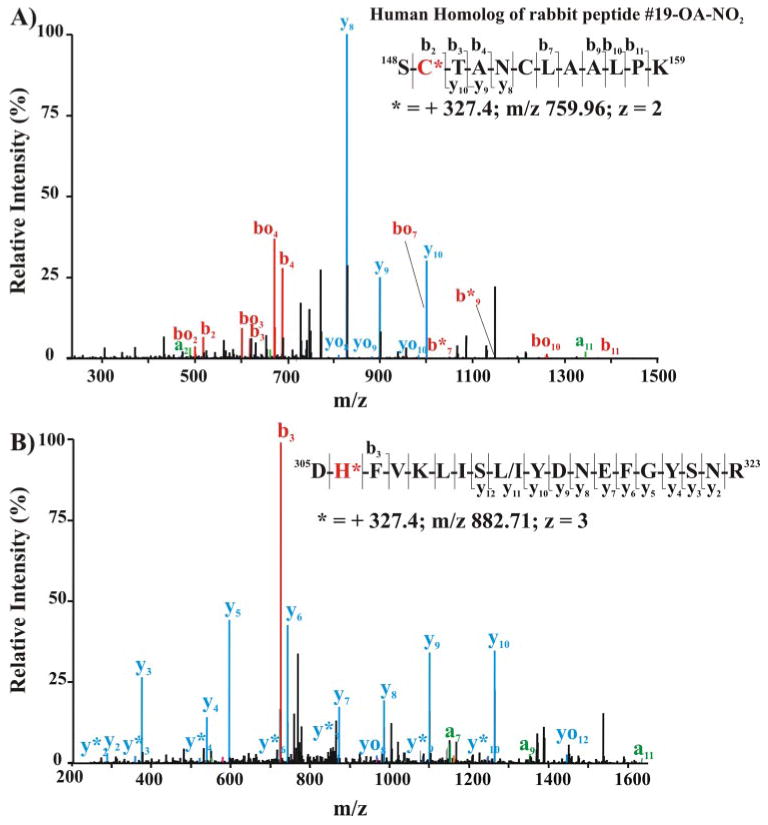
The cytosolic (A) and membrane-associated (B) protein fractions from lysed red cells were separated by SDS-PAGE using nonreducing, denaturing conditions (4–15% gradient gel). The 36-kDa Coomassie dye-binding band corresponding to the Rf of GAPDH was excised and digested in-gel with sequencing grade trypsin. Peptides were extracted, separated, and analyzed by LC nanospray linear ion trap MS/MS (LTQ; Thermo Electron Corp.). A, MS/MS of the doubly charged ion at m/z 759.96 corresponding to the human homolog of rabbit nitroalkylated peptide 19. Inset, amino acid sequence indicating major C- and N-terminal fragment ions detected by full-scan MS/MS. B, MS/MS spectrum of triply charged human GAPDH ion at m/z 882.71 corresponding to the human peptide sequence 305–323. Inset, amino acid sequence indicating major C- and N-terminal fragment ions detected by full-scan MS/MS.
