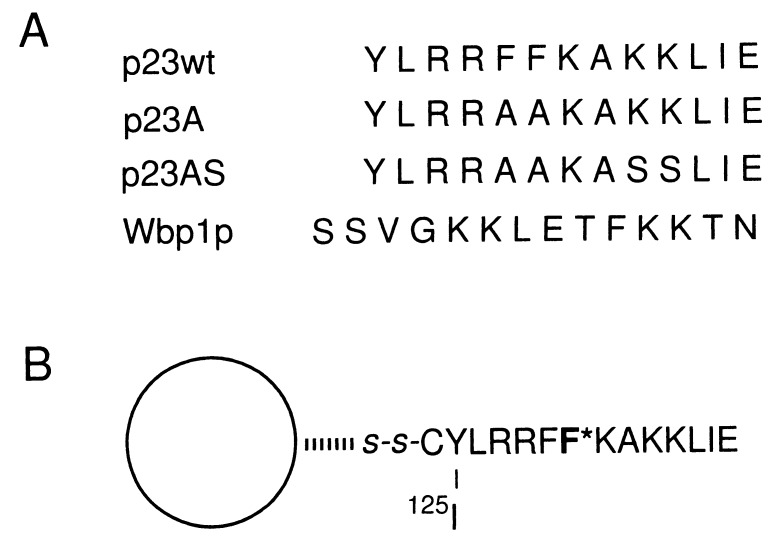
Figure 1.
Peptides used in this study. (A) Peptide sequences of p23wt, p23A, p23AS, and Wbp1p. p23wt represents the cytoplasmic domain of p23 known to bind coatomer. p23A binds coatomer less efficiently than the wild-type peptide, whereas the peptide p23AS has lost this capability. Wbp1p represents the cytoplasmic domain of a subunit of the yeast N-oligosaccharyltransferase complex and contains a characteristic KKXX ER-retrieval motif also known to interact with coatomer. (B) Immobilized, photoreactive p23wt peptide (125I-F*-p23wt). The natural Phe at position −8 was replaced by the photoreactive analogue l-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl-3H-diazirin-3-yl)]phenylalanine (F*, Tmd-Phe). F*-p23wt peptide was immobilized by coupling to thiopropyl-Sepharose by a disulfide bond and was radioactively labeled with [125I]iodine.