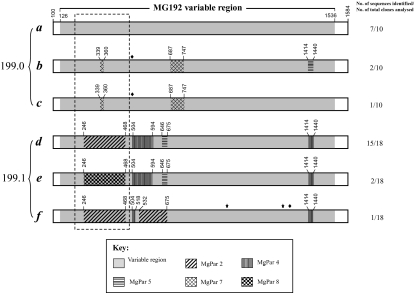
Fig. 4.
representation of MG192 sequence variation and rapid shift identified in two sequential samples (No. 199.0 and 199.1) obtained 10 days apart from an M. genitalium-infected patient. A total of six MG192 variants (a to f) were identified from these two specimens, with three variants present in each specimen. The sequence of the variant a, which is the most predominant variant from the first specimen, is considered the prototype. Various patterns in other five variants represent regions that are different from the variant a and instead have homology to MgPars identified in this patient, as indicated by the key. The diamond indicates single-nucleotide substitutions, which can be traced to a specific MgPar sequence, whereas the star indicates single-nucleotide substitutions, which are not present in any other MG192 variants or MgPars. Numbers above each region refer to the nucleotide positions in the full-length MG192 of the variant a. Detailed nucleotide sequences for the regions included in the box with dashed lines are given in Fig. 6. The number of plasmid clones analysed for MgPars in the patient specimens is listed in Table 3. All clones analysed for each MgPar showed the same sequence except for the triplet repeat number variation in MgPars 2 and 8. The sequences of MG192 variants a to f and MgPars 1 through 9 identified from this patient's strain have been submitted to GenBank under Accession No. EF117283 to EF117288 and EF117293 to EF117301 respectively.