Figure 1.
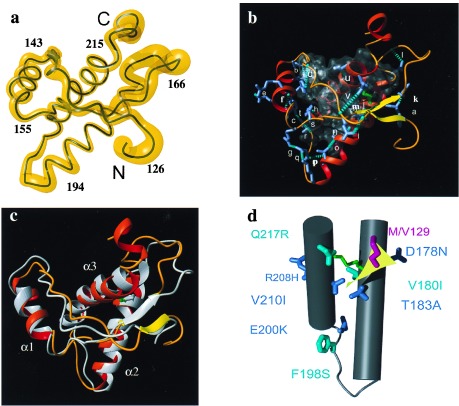
Global features of the refined NMR structure of mPrP(121–231). (a) Backbone of residues 126–226 of the mean structure of mPrP(121–231) as a spline function through the Cα positions. The variable radius of the yellow cylinder is proportional to the mean global backbone displacement per residue evaluated after superposition of the 20 conformers used to represent the solution structure for best fit of the atoms N, Cα, and C′ of residues 126–166 and 172–226. The chain ends and some sequence locations are indicated. (b) Backbone 126–226 represented with helices as red ribbons, the β-sheet as yellow ribbons, and the loop regions as orange tubes. The disulfide bond Cys-179–Cys-214 is indicated in green. The hydrophobic core containing residues 134, 137, 139, 141, 158, 161, 175, 176, 179, 180, 184, 198, 203, 205, 206, 209, 210, and 213–215 (see text) is shown in a translucent envelope. Outside of the core all hydrogen bonds involving side chains (blue stick models) are represented by dashed cyan cylinders and labeled by a code of lowercase letters that refers to Table 2. (c) Superposition for best fit of the backbone atoms of residues 126–219 of the refined structure in b with the structure from ref. 14, which is drawn in gray. The three helices are identified as α1, α2, and α3. (d) Location of mutations that in the homologous hPrP have been associated with inherited prion diseases (see text). Helices 2 (on the right) and 3 are drawn as gray cylinders, the connecting loop as a gray tube, and the two-stranded β-sheet as a yellow plane. The disulfide bond is identified by green coloring. The mutation sites that segregate with CJD are colored blue, the Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome mutation sites are cyan, and the site of the polymorphism M/V129 is red. The amino acids in the mouse sequence, which are shown here, are in all cases identical to those in the human protein. This figure and Fig. 2 were prepared with the program molmol (45).