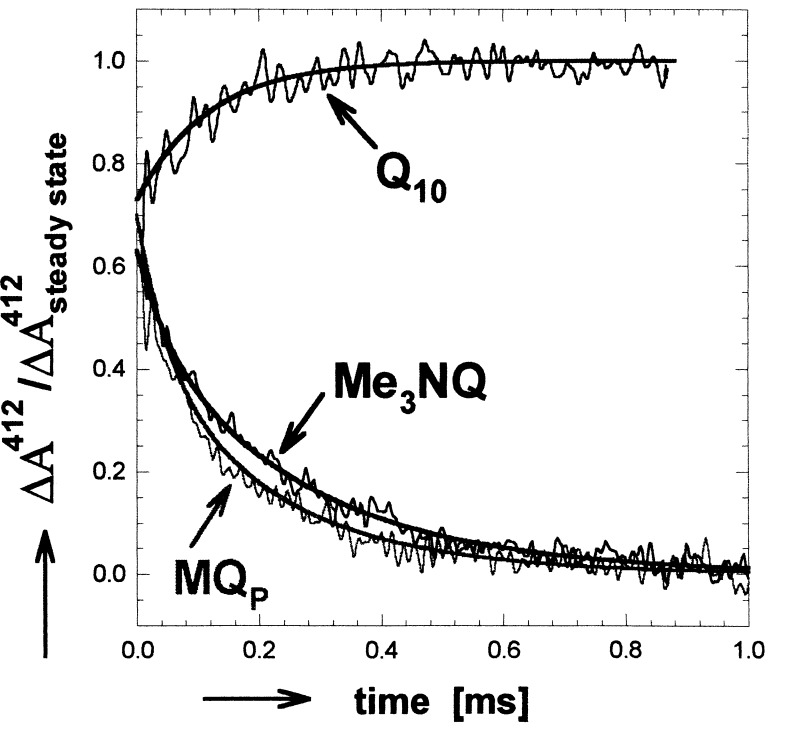
Figure 1.
Optical absorbance changes at 412 nm associated with electron transfer from QA−⋅ to QB in hybrid (Me3NQ−⋅ or MQP−⋅ in the QA site and Q10 in the QB site) and native (Q10 in both QA and QB sites) RCs. In native RCs, the absorbance change is due to an electrochromic shift of the BPhe absorption. In hybrid RCs, the main effect is caused by the difference in extinction coefficient between the naphthosemiquinones (NQ−⋅ in the QA site and Q10−⋅ in the QB site). The observed transients in hybrid RCs are reduced by the electrochromic shift, which was assumed to be the same as that observed in native RCs. The data for the hybrid RCs were normalized to the expected absorption determined from the known difference in extinction coefficients between (NQ)A−⋅ and Q10−⋅ (11, 20, 21). A shallow slope determined by monitoring the recombination reactions (D+QA−⋅ → DQA and D+QAQB−⋅ → DQAQB) was subtracted for clarity. Addition of terbutryne, which inhibits electron transfer to QB, eliminated the transient kinetic phases. [Conditions: 5 μM 2.4.1RCs, BMK buffer (pH = 7.2), 0.03% LDAO. Spectral bandwidth, 10 nm].