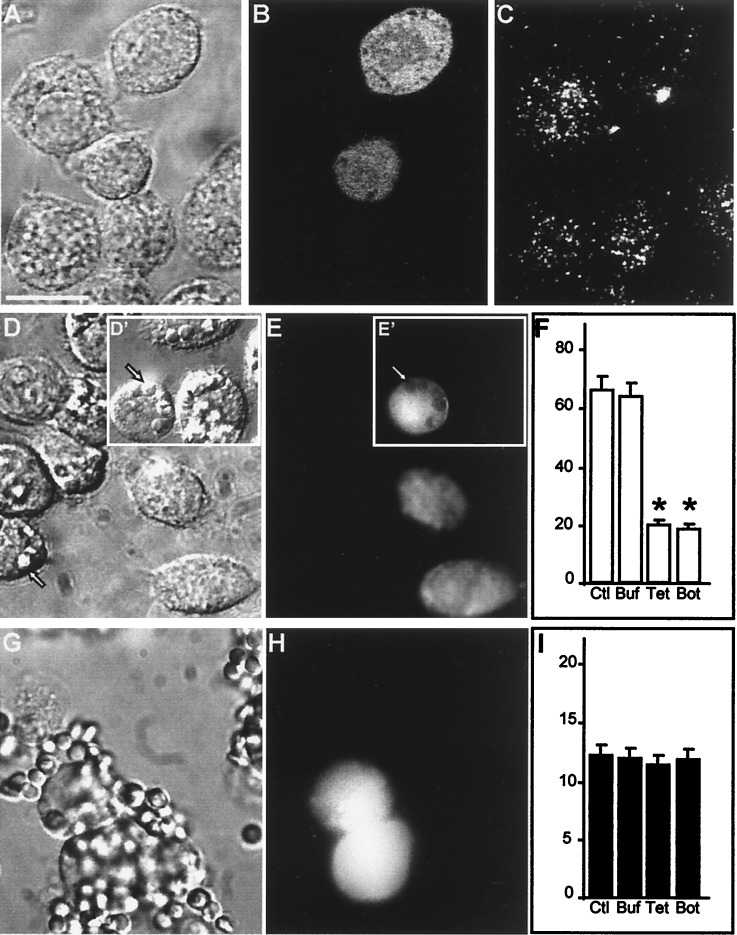
Figure 2.
Impaired phagocytosis after degradation of VAMP-2 in J774 cells. (A–C) J774 cells were injected with TeTx-LC in a solution containing fixable FITC-dextran as a marker of injection. After 5 h of incubation at 37°C, the cells were stained with antibody to VAMP-2. (A) Bright field micrograph. Bar, 10 μm. (B) Green fluorescence (Lucifer yellow emission) of the field shown in A identifying two injected cells. (C) VAMP-2 immunostaining in the cells shown in A. (D–F) J774 cells were injected with tetanus toxin and FITC-dextran as above, then assessed for their ability to perform phagocytosis of opsonized SRBCs. (D) Bright field micrograph. Inset (D′) shows cell injected with dextran alone. Arrow indicates location of representative internalized SRBCs. (E and E′) Green fluorescence emission of the cells shown in D. Arrowhead demonstrates the displacement of FITC-dextran by internalized the SRBCs. (F) Effect of toxin injection on phagocytosis. Data are means ± SE of 250 noninjected control (Ctl) cells, 175 buffer- (Buf) injected controls, 244 TeTx-LC- (Tet) injected cells, and 75 botulinum- (Bot) injected cells (asterisks indicate P < 0.05 vs. Ctl). (G–I) J774 cells were injected with TeTx-LC as above and then assessed for their ability to bind opsonized SRBCs. (G) Bright field micrograph. (H) Fluorescence emission of the cells shown in G identifying injected cells. (I) Effect of toxin injection on SRBC adherence to J774 cells. Data are means ± SE of 165 noninjected control (Ctl) cells, 64 buffer- (Buf) injected controls, 75 TeTx-LC- (Tet) injected cells, and 57 botulinum- (Bot) injected cells. Images are representative of five separate experiments.