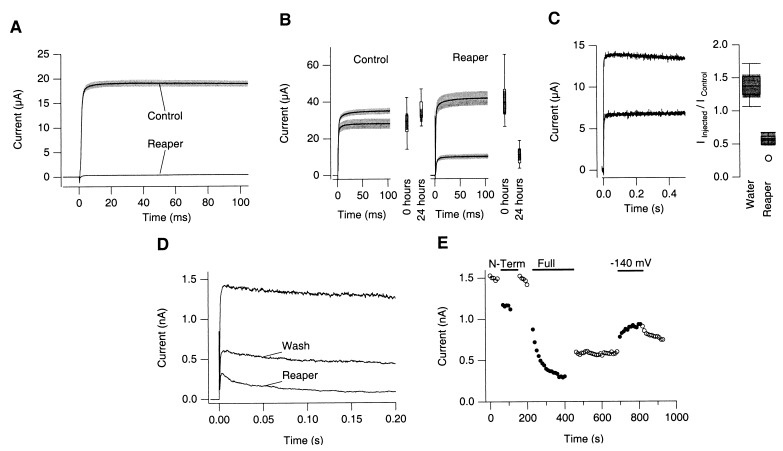
Figure 3.
Effects of full length Reaper protein on the K+ channel. (A) Coinjection of Reaper and ShBΔ6–46:T449V RNAs into Xenopus laevis oocytes inhibits functional expression of the channel. Two-electrode voltage-clamp recordings at +50 mV were made 1 day after injection of the RNAs. Solid lines represent the averaged currents from 13 cells. Shaded areas represent the respective SEM. (B) Reaper RNA injection reduces K+ currents through the ShBΔ6–46:T449V channels already in the membrane. Oocytes were injected with ShBΔ6–46:T449V channel RNA on Day 0. On Day 1, the cells were divided into two groups, and control recordings were made (current amplitudes at 0 hr). Cells then were injected with either Reaper RNA or H2O (control). Currents again were recorded 24 hr later (current amplitude values at 24 hr). Injection of Reaper RNA resulted in significant reduction in current amplitude (right) whereas injection of H2O had no effect (left). Solid lines represent mean currents recorded by using a two-electrode voltage clamp from 10 to 15 cells. Shaded areas represent the respective SEM. (C) Direct injection of synthetic full length Reaper peptide decreases the ShBΔ6–46:T449V current amplitude. Control currents were recorded by using a two-electrode voltage-clamp, and the cells then were injected immediately with either H2O (40 nl) or full length synthetic Reaper protein (40 nl, 1 mM). Cells were allowed to recover for 2 hr after injection, and currents then were recorded from the same cells. Representative currents before and after peptide injection are shown (left). Relative changes in the current amplitudes are compared by using boxplots (right). (D) Synthetic full length Reaper peptide induces inactivation in the ShBΔ6–46:T449V K+ channel. Macroscopic currents recorded from one patch are shown. The control current, the current recorded in response to the 18th pulse in the presence of Reaper, and the current after wash-out are shown. Depolarizing pulses to +50 mV were applied every 10 s. (E) The effect of synthetic full length Reaper is near irreversible. Peak macroscopic ShBΔ6–46:T449V current amplitudes recorded from one inside-out patch in response to repeated depolarizing pulses to +50 mV from a holding potential of −90 mV at 10-s intervals are shown. Synthetic Reaper N terminus peptide (100 μM) and full length Reaper synthetic peptide (100 μM) were applied to the intracellular side of the patch. The block induced by the short N terminus peptide (N-term) was completely reversible by washing the chamber with peptide-free solution. In contrast, channel block induced by full length Reaper peptide (Full) was only partially reversible. Hyperpolarization to −140 mV resulted in only a slight increase in peak current amplitude.