Figure 11.
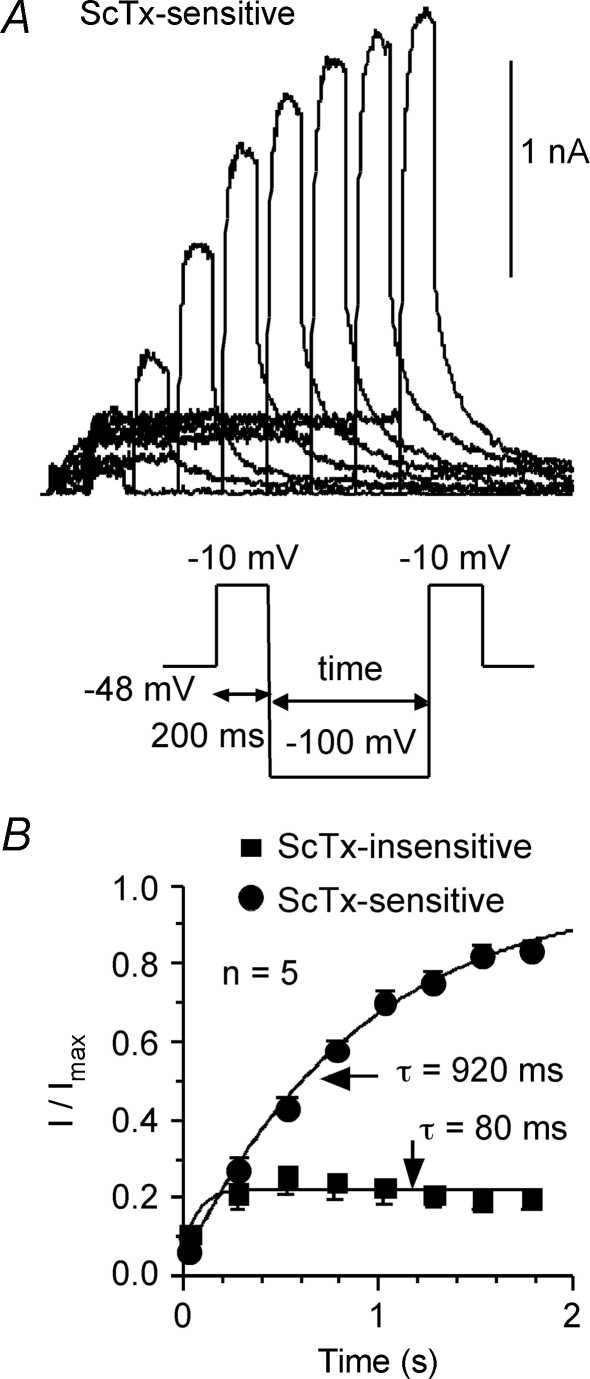
Recovery from inactivation of the ScTx-sensitive currents was tested in 5 cells using a protocol shown in the lower part of A The currents were inactivated at a holding potential of −48 mV. A 200 ms test pulse of −10 mV was delivered and followed by a recovery voltage step of −100 mV. The duration of the recovery voltage step varied from 0.02 to 1.77 s with increments of 0.25 s. A second test pulse of −10 mV was delivered after the recovery voltage step. Currents in response to the second test pulse were analysed relative to the first test step. A, typical example of the recovered ScTx-sensitive currents (P30). B, the peak recovered ScTx-sensitive currents can be well fitted by an exponential function, yielding a recovery time constant of 920 ms. Similar data were obtained for the AB-sensitive current (see text). The recovery time constant for the ScTx-insensitive component was 170 ms.