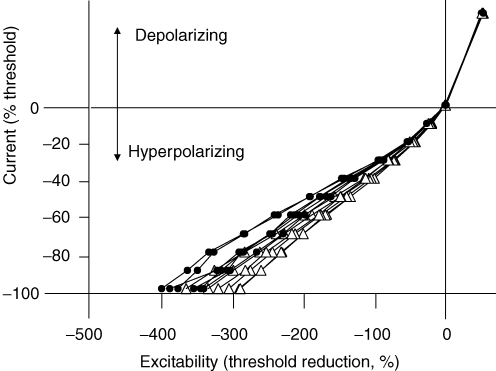
Figure 4.
There is reduced accommodation of motor axons to hyperpolarizing currents of 50–300 ms duration on the affected side of patients Accommodation to hyperpolarization was assessed in six patients measuring the threshold changes 50, 100, 150, 200, 250 and 300 ms after the onset of the polarizing current. Accommodation to depolarizing currents was complete within 50 ms (see Fig. 2) and, accordingly, the data points for the different current durations superimpose (top right panel). In the hyperpolarizing direction, the greater the current duration the greater were the threshold changes due to slow electrotonus and the slowly activated inwardly rectifying accommodation to the hyperpolarization. There was significantly reduced inward rectification for the affected side (•) compared to the unaffected side (▵) regardless of the duration of the polarizing stimulus.