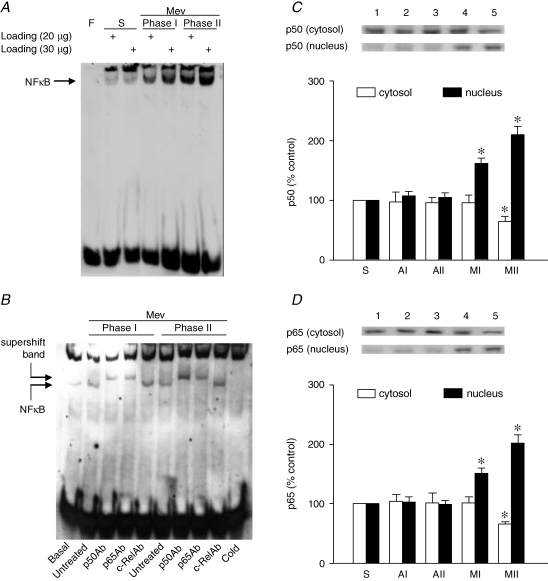
Figure 4.
EMSA and Western blot analysis of nucleus-bound translocation of NF-κB in ventrolateral medulla during Mev intoxication A, representative gel depicting NF-κB DNA binding in nuclear extracts from the ventrolateral medulla of sham-controls (S or Basal), or during Phases I or II cardiovascular responses to Mev (10 nmol). Note that two sample-loading volumes were used to validate our results. F, free probe. B, NF-κB DNA binding in nuclear extracts from the ventrolateral medulla pre-incubated in the absence (untreated) or presence of antiserum against p50, p65 or c-Rel subunit of NF-κB. A competitive assay with the addition of 100-fold unlabelled NF-κB oligonucleotide was used to control for non-specific binding (Cold). C and D, temporal changes as percentage relative to sham-controls (S) of cytosolic and nuclear content of NF-κB p50 or p65 subunit in the ventrolateral medulla of animals 30 min (AI or MI) or 180 min (AII or MII) after animals received bilateral microinjection into RVLM of aCSF or Mev (10 nmol). Values are mean ± s.e.m. of triplicate analyses on samples pooled from 5 to 6 animals in each group. *P < 0.05 vs. sham-control or corresponding aCSF group in the Scheffé's multiple-range analysis.