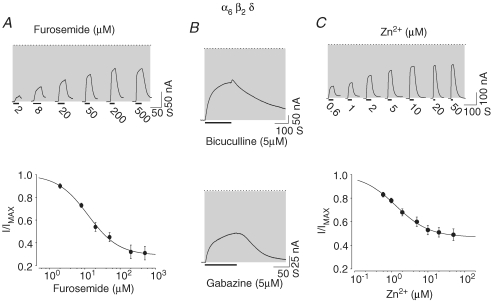
Figure 2.
Furosemide, bicuculline, gabazine and Zn2+ inhibit the spontaneous current arising from α6β2δ receptors A, furosemide blocked the spontaneous activity of α6β2δ receptors. Current traces and the concentration–response relationship for furosemide-dependent inhibition of the spontaneous current arising from an oocyte with a high level of expression of α6β2δ receptors. The dotted line indicates the zero-current level; the shaded area represents the spontaneous activity. The thick lines below the current traces represent the duration of antagonist application. B, bicuculline and gabazine inhibited the spontaneous activity of α6β2δ receptors. Current traces representing bicuculline (5 μm) and gabazine (5 μm) inhibitory action on the spontaneous activity. C, the representative current traces and concentration–response relationship for Zn2+ block of the spontaneous current arising from α6β2δ receptors.