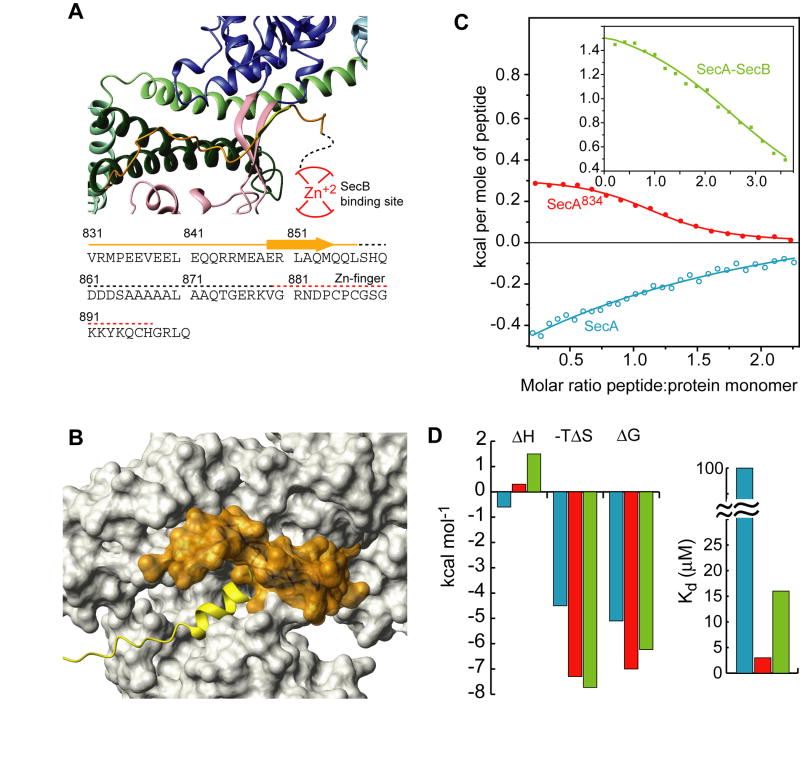
Figure 5. Inhibition of signal peptide binding by the C-tail of SecA.
(A) View of the C-tail of B. subtilis SecA (PDB 1M6N). This is the only crystal structure wherein part of the C-tail is resolved. The E. coli SecA sequence of the C-tail is shown below the model. Dotted lines indicate crystallographically unresolved regions. Red lines indicate the zinc-finger region, which is the primary SecB binding site.
(B) Structural modeling of the interaction of the C-tail in E. coli SecA. The C-tail is shown in orange surface and it partially occludes the peptide binding groove.
(C) Binding isotherms of the calorimetric titration of the wild-type LamB signal peptide to SecA (open, cyan circles), SecA834 (filled, red circles), and SecA bound to SecB (green squares).
(D) Thermodynamic parameters of the calorimetric titrations in (C) displayed as bars. The color code is as in (C).