Figure 5.
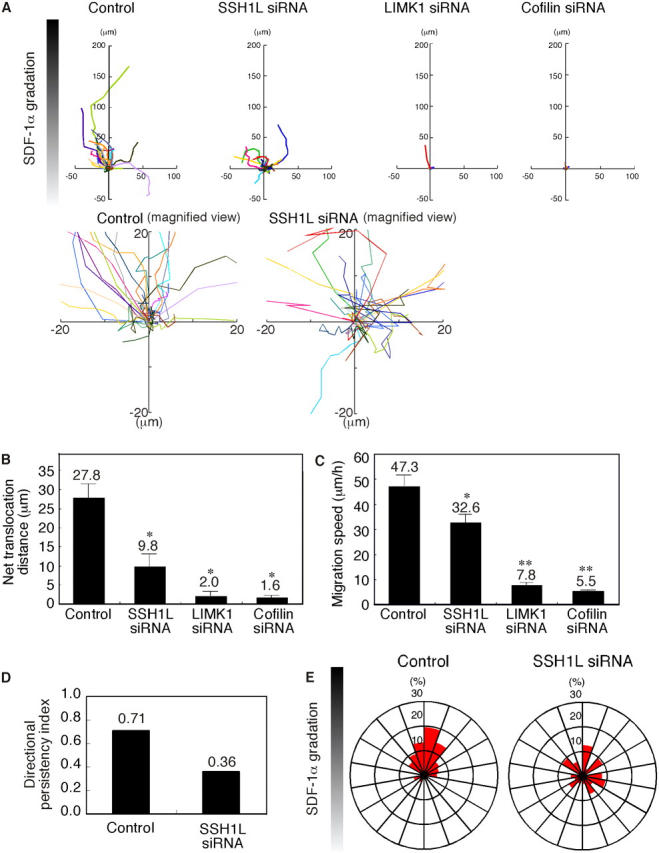
Effect of SSH1L, LIMK1, or cofilin siRNA on SDF-1α–induced T cell chemotaxis in Dunn chambers. Jurkat cells were transfected with siRNA plasmids for SSH1L, LIMK1, cofilin, or empty plasmid (control) and were analyzed for their ability to migrate in an SDF-1α gradient in the Dunn chamber during a 50-min period. (A) The migration paths of 30 randomly chosen cells were traced for 50 min. The intersection of the x and y axes was taken to be the starting point of each cell path, whereas the source of SDF-1α was at the top. Magnified views of the paths of control cells and SSH1L siRNA cells are also shown. (B) The net translocation distance (straight distance from the start to the end point) of each cell over the 50-min period is shown as the mean ± SEM (error bars) of the paths of 50 randomly chosen cells. *, P < 0.01 compared with control cells. (C) The migration speed (total length of the migration path per hour) of each cell is shown as the mean ± SEM of the paths of 50 randomly chosen cells. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 compared with control cells. (D) The directional persistency index (the ratio of the net translocation distance to the cumulative length of migration path) of control and SSH1L siRNA cells. (E) Circular histograms showing the percentage of cells whose final position was located within each of 18 equal sectors (20°). The source of SDF-1α was at the top. Data from control and SSH1L siRNA cells are shown.
