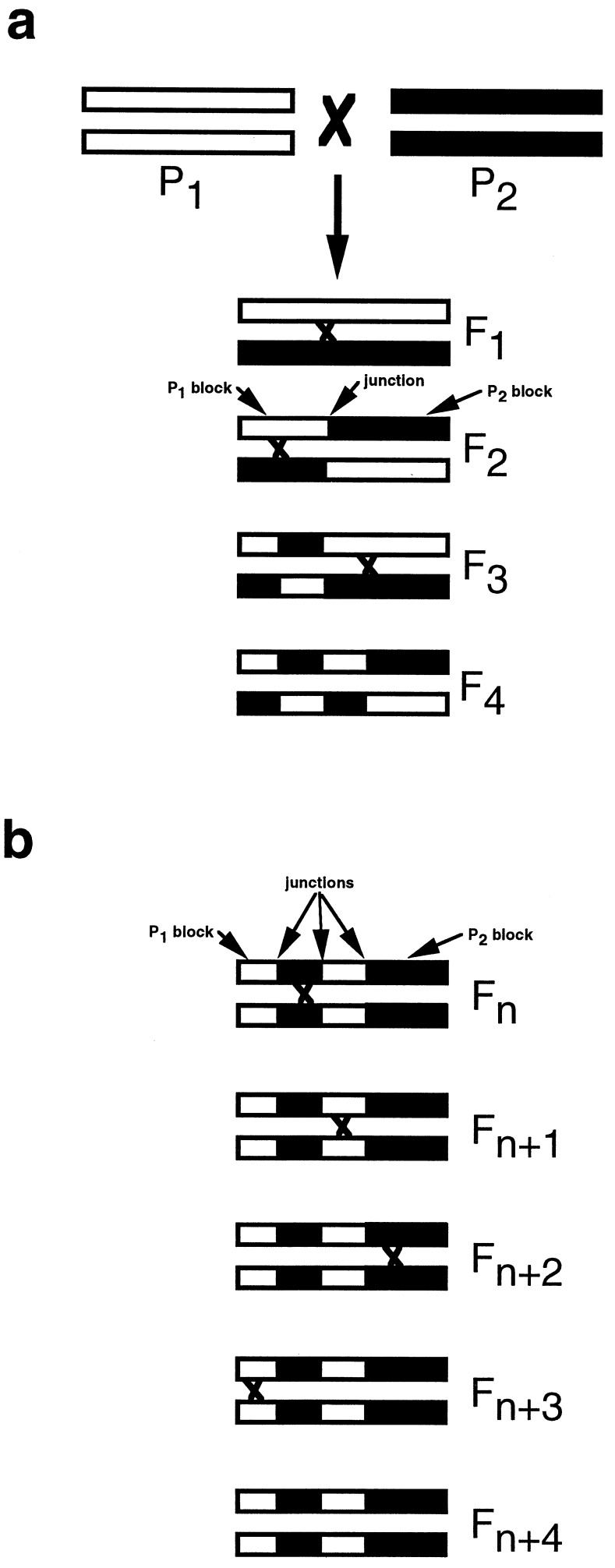
Figure 1.
Illustration of the reduction and fixation of parental chromosomal blocks (black vs. white) over successive generations of hybridization. Chiasmata, and hence junction origin, are designated by “x”s between intra-generational chromosomes. (a) Hypothetical scenario demonstrating how parental species chromosomal block size decreases and junction number increases over successive generations of hybridization. (b) When genomic composition becomes fixed or stabilized, no further reduction in block size can occur, despite continued recombination in successive generations.