Figure 5.
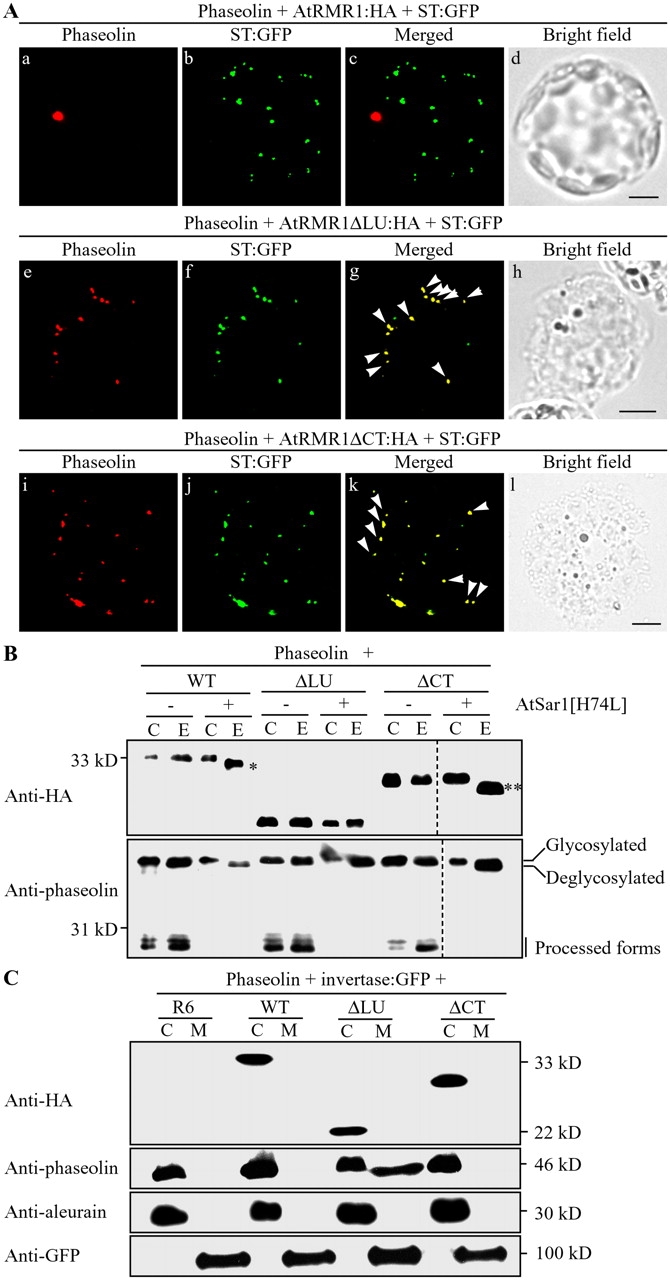
Phaseolin accumulates in the Golgi complex in the presence of deletion mutants. (A) Localization of phaseolin in the presence of deletion mutants. Protoplasts were transformed with the indicated constructs, and localization of phaseolin was examined. Phaseolin was detected from the fixed protoplasts with antiphaseolin antibody, whereas the GFP signals of ST-GFP were directly observed. Arrowheads indicate overlaps between the indicated proteins. Bars, 20 μm. (B) EndoH resistance of the glycan moiety of phaseolin in the presence of AtRMR1 deletion mutants. Protein extracts were obtained from protoplasts transformed with the indicated constructs, treated with endoH, and analyzed by Western blotting using antiphaseolin and anti-HA antibodies that detect phaseolin and HA-tagged AtRMR1 deletion mutants, respectively. Single and double asterisks indicate deglycosylated forms of AtRMR1-HA and AtRMR1ΔCT-HA, respectively. C, control protein extracts; E, endoH-treated protein extracts. Dotted lines indicate that two separate images were brought together to generate a single composite image. (C) Secretion of phaseolin in the presence of coexpressed AtRMR1ΔLU-HA. Phaseolin and invertase-GFP were coexpressed in protoplasts together with the indicated AtRMR1 constructs. Proteins secreted from the protoplasts were prepared from the incubation medium (M). In addition, protein extracts were prepared from the transformed protoplasts (C). Phaseolin, endogenous aleurain, and invertase-GFP were detected using antiphaseolin, antialeurain, and anti-GFP antibodies, respectively. HA-tagged AtRMR1 deletion mutants were detected with anti-HA antibody. R6, an empty vector; WT, wild-type AtRMR1; ΔLU, AtRMR1ΔLU-HA; ΔCT, AtRMR1ΔCT-HA.
