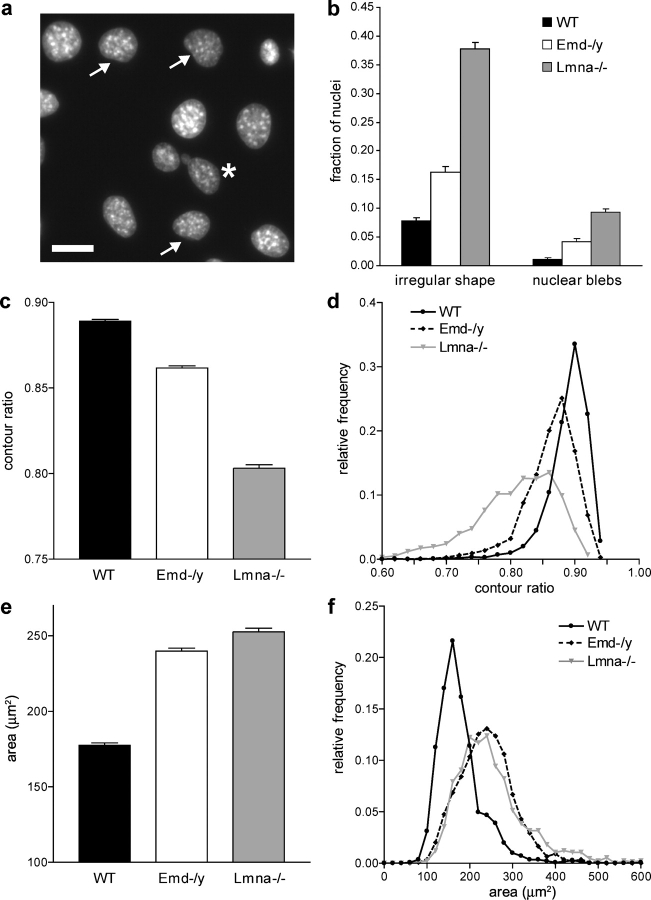
Figure 2.
Emerin and A-type lamin-deficient fibroblasts have abnormal nuclear shape. (a) Fluorescently labeled nuclei of emerin-deficient mouse embryo fibroblasts. Asterisk denotes nucleus with chromatin protruding from the nucleus (nuclear bleb). Arrows indicate nuclei that have mild deviations from the typical round shape. Bar, 20 μm. (b) The fraction of abnormally shaped nuclei and nuclear blebs was significantly increased in emerin and A-type lamin-deficient fibroblasts, with emerin-deficient cells displaying a milder phenotype (cell fractions with abnormal nuclear shape were 0.077 ± 0.006 for wild-type, 0.163 ± 0.009 for emerin-deficient, and 0.378 ± 0.011 for A-type lamin-deficient cells, P < 0.0001 for emerin-deficient and A-type lamin-deficient cells compared with wild-type cells; cell fractions with nuclear blebs were 0.012 ± 0.002, 0.042 ± 0.005, and 0.093 ± 0.006 for wild-type, emerin-deficient, and A-type lamin-deficient cells, respectively, P < 0.0001 for emerin-deficient and A-type lamin-deficient cells compared with wild-type cells; n ∼1,800 for each cell type). (c) Emerin-deficient cells have a significantly decreased contour ratio compared with wild-type cells, but display a milder phenotype compared with A-type lamin-deficient cells (contour ratio = 0.89 ± 0.004 for wild-type, 0.86 ± 0.006 for emerin-deficient, and 0.80 ± 0.007 for A-type lamin-deficient cells, P < 0.001 for emerin-deficient and A-type lamin-deficient cells compared with wild-type; n ∼1500 for each cell type in three independent experiments). (d) Relative frequency distribution of the contour ratio for wild-type, emerin-deficient, and A-type lamin-deficient cells (median values were 0.896, 0.869, and 0.817 for wild-type, emerin-deficient, and A-type lamin-deficient cells, respectively). The difference in the medians was statistically significant (P < 0.001 for emerin-deficient and A-type lamin-deficient vs. wild-type). (e) Emerin and A-type lamin-deficient cells have significantly increased nuclear cross-sectional areas compared with wild-type cells (Nuclear cross-sectional area = 178 ± 4.5 μm2, 252 ± 24.7 μm2, and 259 ± 25.6 μm2 for wild-type, emerin-deficient, and A-type lamin-deficient cells, respectively, P < 0.01 for emerin and A-type lamin-deficient compared with wild-type cells, n ∼1500 for each cell type in three independent experiments). (f) Frequency distribution of the cross-sectional area for wild-type, emerin-deficient, and A-type lamin-deficient cells.