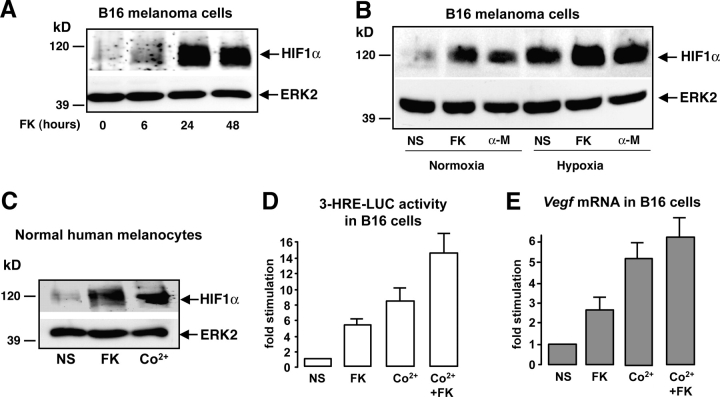
Figure 1.
cAMP increases the expression of a functional HIF1α protein in melanocyte cells. (A) B16 cells were stimulated for 6, 24, and 48 h with forskolin (FK) and cell extracts were subjected to Western blot analysis to detect HIF1α protein levels. A control of the protein loading was performed by detecting ERK2. (B) The same experiment was performed by stimulating B16 cells either with forskolin (FK) or α-MSH (α-M) for 24 h. Cells were incubated, either in normal oxygen conditions (Normoxia, 20% O2) or maintained under hypoxia (1–2% O2). (C) A Western blot to analyze HIF1α protein expression was performed using extracts from normal human melanocytes. Cells were starved and treated with forskolin (FK) for 24 h or with cobalt (Co2+) to mimic hypoxia as a positive control. (D) B16 cells were transfected with the 3-HRE-LUC reporter construct and treated (or not) (NS) with forskolin (FK) for at least 36 h, with cobalt (Co2+) for 12 h, or with both (Co2+ + FK). Luciferase activity was normalized by the β-galactosidase activity and data are expressed in fold stimulation of the basal 3-HRE-LUC activity. Data are means ± SE of five experiments performed in triplicate. (E) Real-time quantitative PCR to detect Vegf mRNA levels on total RNA extracts from B16 cells treated as described in D.