Figure 2.
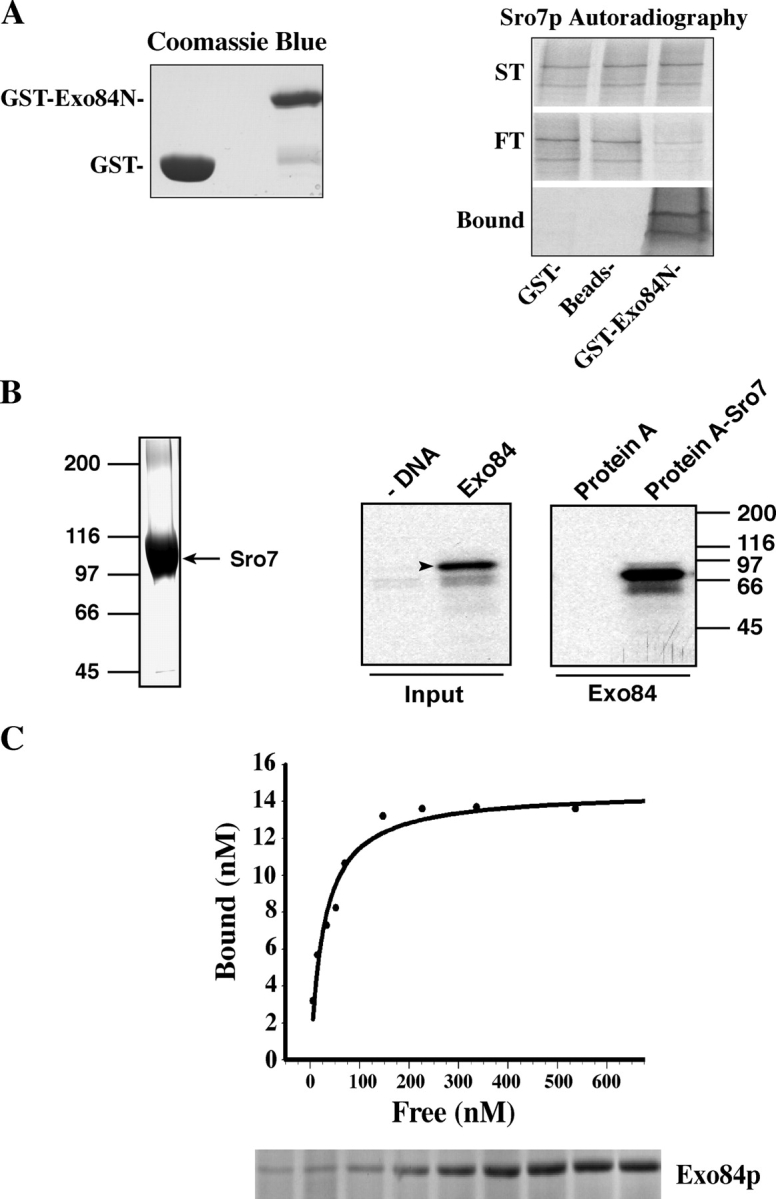
Sro7p interacts with Exo84p in vitro. (A) Sro7p specifically binds to the NH2 terminus of Exo84p in vitro. The NH2 terminus of Exo84p (aa 1–320) was expressed as a GST fusion protein and was immobilized to glutathione–Sepharose 4B; Sro7p was in vitro translated in the reticulocyte lysate system in the presence of [35S]methionine. The proteins as well as controls (GST–Sepharose beads and unconjugated Sepharose beads) were used in the binding reaction. The starting materials (ST), bound, and unbound (FT) Sro7p were analyzed by electrophoresis and autoradiography. (left) Coomassie blue staining of input GST and GST-Exo84N fusion protein. (B) Protein A–Sro7 recombinant protein was expressed in yeast and was purified by IgG–Sepharose beads. An aliquot of the fusion protein that bound to Sepharose beads was shown in the Coomassie blue–stained gel (left). Full-length Exo84p was in vitro transcribed and translated in the presence of [35S]methionine (arrowhead). Exo84p that bound to the Sepharose beads was shown in the autoradiograph. 50% of input Exo84p used in this binding assay is shown to the left. As a control, protein A–Sepharose beads were used in the binding reaction. (C) The dissociation constant of Sro7p–Exo84p interaction. Protein A–Sro7p was purified from yeast and was conjugated to IgG–Sepharose beads. Various amounts of purified GST-Exo84N were incubated with protein A–Sro7p Sepharose beads for the binding reaction. The protein samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE, and the gels were stained by Coomassie blue. Bound and free GST-Exo84N were quantified and plotted with a single rectangular hyperbola equation (B = BmaxC/[Kd + C]) by using SigmaPlot software. (bottom) Bound GST-Exo84N stained by Coomassie blue.
