Figure 5.
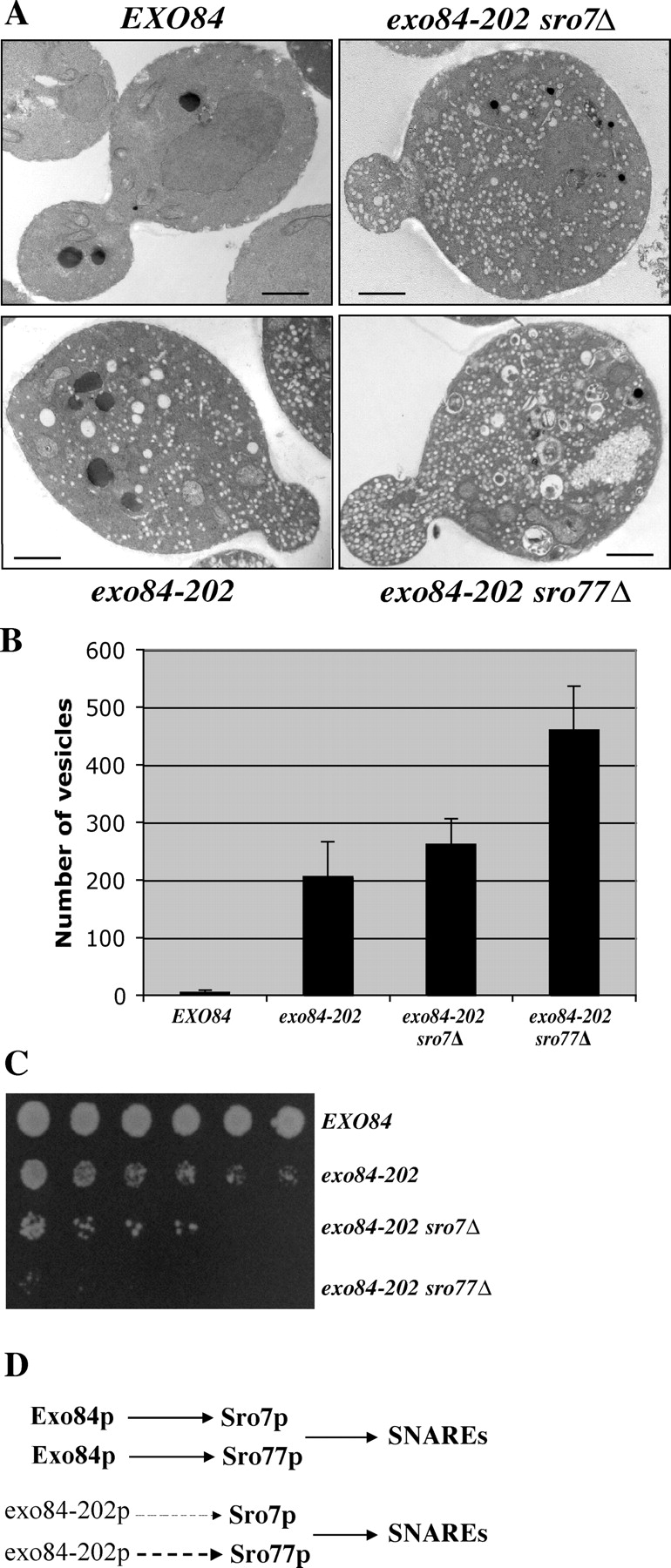
Growth defects and accumulation of post-Golgi secretory vesicles in exo84-202 and sro7/77 mutants. (A) Wild-type, exo84-202, exo84-202 sro7Δ, and exo84-202 sro77Δ cells were grown to early log phase at 25°C, shifted to 37°C for 2 h, and processed for thin-section EM. Bars, 1 μm. (B) Quantification of the number of secretory vesicles/section in the wild-type and mutant cells (n = 20). Error bars represent SD. (C) Growth of wild-type, exo84-202, exo84-202 sro7Δ, and exo84-202 sro77Δ cells on the yeast extract/peptone/glucose plate at 34°C. The yeast cells were plated in 1:10:20:40:80:160 dilutions. (D) Exo84p interacts with both Sro7p and Sro77p in the cells, forming parallel pathways that regulate SNARE assembly. The exo84-202 protein maintains a weak interaction with Sro77p (dashed line) and an even weaker interaction with Sro7p (thin dashed line). Deletion of SRO7 or SRO77 in the exo84-202 strain background further disrupts the pathway, leading to more severe growth and secretion defects.
