Figure 5.
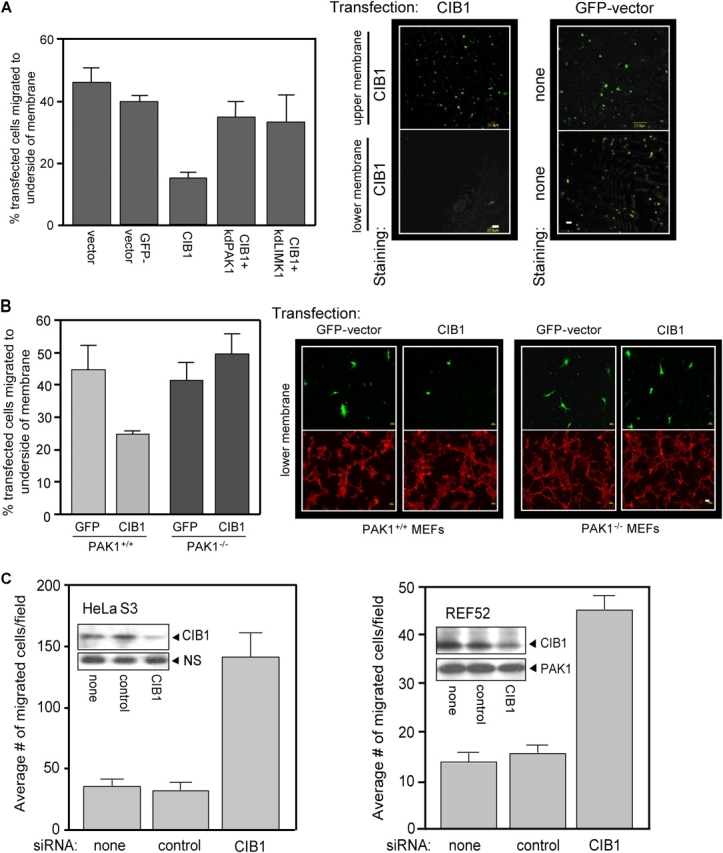
CIB1 overexpression inhibits, and endogenous CIB1 depletion increases, cell migration. (A) Serum-starved REF52 cells transfected with GFP vector, control vector, or CIB1 ± kdPAK1 or kdLIMK1 were subjected to haptotactic transwell migration assays toward FN. Transfected cells on either the top membrane (nonmigrating cells) or bottom membrane (migrating cells) were visualized by staining for CIB1 expression (middle). Control migration was visualized by GFP fluorescence (right). Cells overexpressing vector CIB1 ± kdPAK1 or ± kdLIMK1 on the top and bottom membranes were also stained as described in migration assays and were counted. Migration is represented as the percentage of the total number of transfected cells from the upper and lower membranes (left). Data represent means ± SEM (n = 3). (B) MEFs derived from wild-type (PAK+/+) and PAK1-null (PAK−/−) mice were transfected with GFP vector or CIB1. Serum-starved cells were assayed for haptotactic migration toward 3 μg/ml FN, and migration was determined as in A (left). Data represent means ± SEM (n = 4). Right panels show representative images of migrated transfected cells (green, top) and phalloidin staining from the same field (red, bottom). (A and B) Bars, 20 μm. (C) HeLaS3 (left) and REF52 (right) cells were mock transfected or transfected with control or specific CIB1 siRNA and subjected to haptotactic transwell migration assays toward FN (as in A). Data represent means ± SEM (error bars; n = 4 for each cell type). Inset blots show representative endogenous CIB1 protein expression and nonspecific (NS) band or PAK1 expression from the same blot as the loading control.
