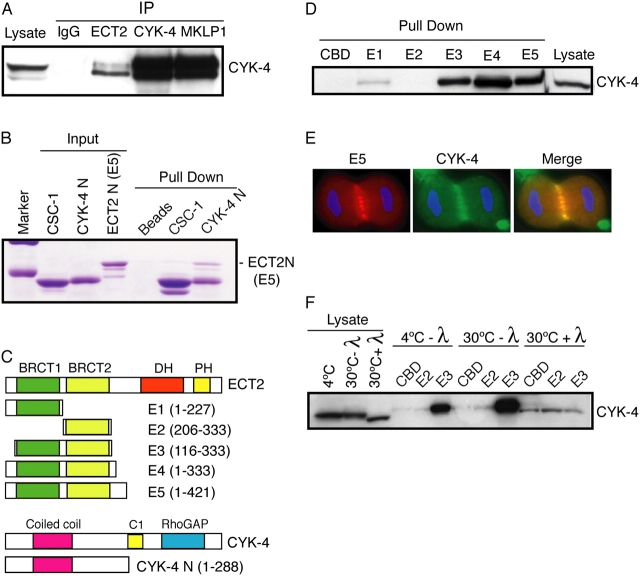
Figure 7.
CYK-4 and ECT2 directly interact and associate in vivo in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. (A) ECT2, CYK-4, and MKLP1 were precipitated and the immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blotting with anti–CYK-4 antibodies. (B) Recombinant, soluble ECT2 E5 was incubated with CBD beads or CBD beads bound to CBD-CYK-4-N or CBD-CSC-1. Bound proteins were analyzed by Coomassie staining. (C) Schematic showing the boundaries of deletion constructs. (D) The tandem BRCT domains are sufficient for efficient binding of CYK-4. E. coli–expressed derivatives bound to chitin beads were used to pull-down proteins from a mitotic cell lysate. Bound proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with anti–CYK-4 antibodies. (E) The ECT-2 truncation derivative E5 colocalizes with CYK-4. Myc-tagged ECT2 E5 construct was transfected into HeLa cells, fixed, and stained for myc and CYK-4. (F) The association between CYK-4 and the ECT2 BRCT domains is phosphodependent. Mitotic cell lysates were treated with λ phosphatase before binding to chitin beads loaded with the indicated proteins. Bound proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with anti–CYK-4 antibodies.