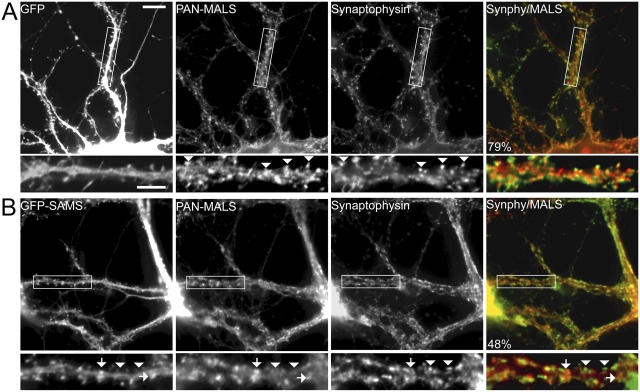
Figure 5.
A dominant-negative liprin-α disrupts presynaptic localization of MALS. Hippocampal cultures (35 DIV) were infected with Semliki Forest virus expressing either GFP or GFP fused to the SAM domains of liprin-α2. Whereas infection and expression of GFP had no effect on synaptic expression of MALS (A, arrowheads), expression of the dominant-negative (GFP-SAM) construct misdirected MALS to nonsynaptic sites (B, arrows) and resulted in a loss of presynaptic MALS (B, arrowheads). Quantification of immunofluorescence reveals that colocalization of MALS (red in overlayed images) with synaptophysin (green in overlayed images) is significantly reduced in neurons expressing GFP-SAM, from 77.3% ± 3.6 in uninfected neurons to 48.1% ± 2.1 and to 79.5% ± 2.0 in GFP-expressing neurons (P < 0.01). Bars: (top) 20 μm; (bottom) 10 μm.