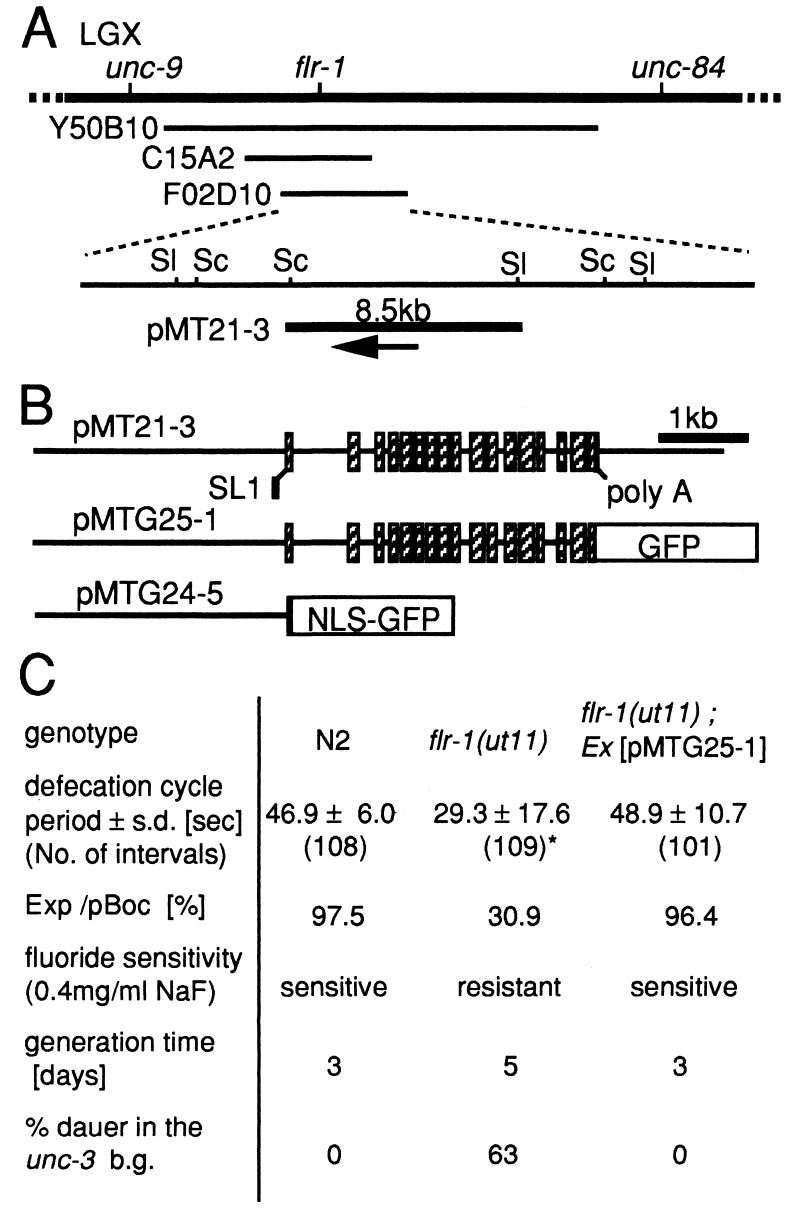
Figure 2.
Cloning of flr-1 gene and cDNA. (A) Genetic and physical map around flr-1 gene. A genomic DNA fragment flanking the transposon Tc1 that caused the flr-1(ut11) mutation, hybridized to the yeast artificial chromosome Y50B10 and the cosmid C15A2. An overlapping cosmid F02D10 and its subclone pMT21–3 rescued the flr-1 phenotypes by microinjection. The arrow shows the direction of transcription of the only complete ORF contained in pMT21–3. Sl, SalI site; Sc, SacI site. (B, Top) The structure of the 8.5-kb genomic clone (pMT21–3) that rescued the flr-1 phenotypes. The 17 exons are indicated by boxes. The trans-splice leader SL1 and the poly(A) tail also are shown. (Middle) The structure of pMTG25–1, which codes for a GFP(F64L S65T)-tagged FLR-1 protein. (Bottom) The structure of pMTG24–5, a flr-1∷GFP(S65C) fusion gene containing a nuclear localization signal. (C) Rescue of various phenotypes of flr-1(ut11) by pMTG25–1.