Figure 1.
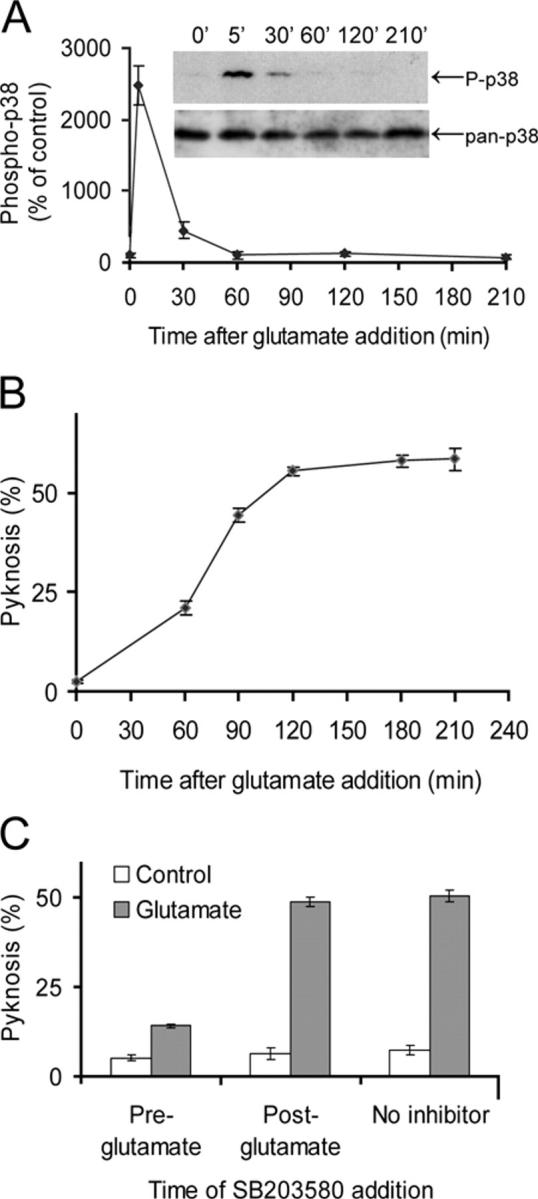
Glutamate-induced neuronal death requires the early phase of p38 activation. (A) Phospho-p38 levels in cerebellar granule neuron extracts prepared at times indicated after exposure to 50 μM glutamate. Phosphorylated p38 levels increase rapidly and fall to basal levels from 60 min after glutamate exposure. The pan-p38 blot indicates equal loading of samples. Means ± range are shown (n = 2). (B) Pyknosis of cerebellar granule neurons was assessed at times indicated after the start of a 30-min glutamate exposure. The pyknosis is complete 2–3 h after exposure to 50 μM glutamate. Means ± SEM are shown (n = 3). (C) Pyknosis was assessed 3 h after a 30-min glutamate exposure, in the presence of 1 μM SB203580, to specifically inhibit p38, added either 30 min before the start or immediately after the end of the 30-min glutamate exposure. Only pretreatment with inhibitor prevented the pyknosis. Means ± SEM are shown (n = 3).
