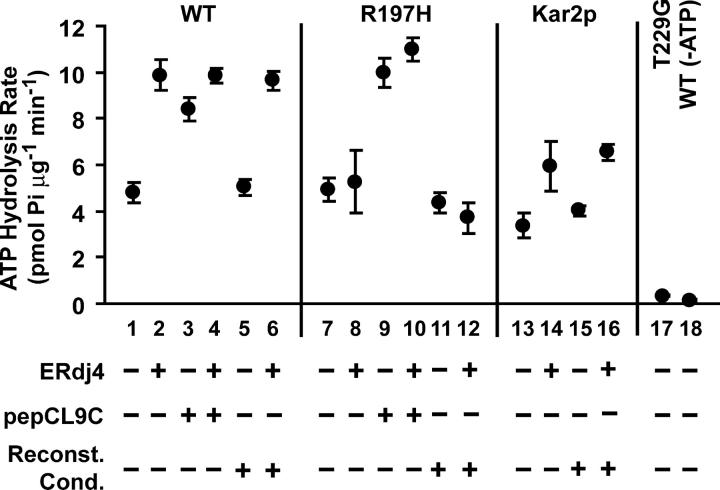
Figure 1.
ATP hydrolysis rates of rBiP derivatives. Inorganic phosphate production was measured spectroscopically to determine rates of steady-state ATP hydrolysis by purified rBiP variants (WT, R197H, T229G) or Kar2p. Measurements were conducted under basal conditions (lanes 1, 7, 13, and 17) or in the presence of purified ERdj4 J domain (fourfold molar excess, lanes 2, 8, and 14), pepCL9C (200-fold molar excess, lanes 3 and 9), or both (lanes 4 and 10), as indicated. Control reactions contained the ATPase mutant rBiP T229G (lane 17) or rBiP WT in the absence of ATP (lane 18). To determine the effect of reconstitution conditions on BiP ATPase activity, rBiP (and ERdj4, where indicated) was exposed to high pH (lanes 5, 6, 11, 12, 15, and 16) before being returned to neutral pH. The mean values from 3–5 independent experiments are shown ± SD.