Figure 2.
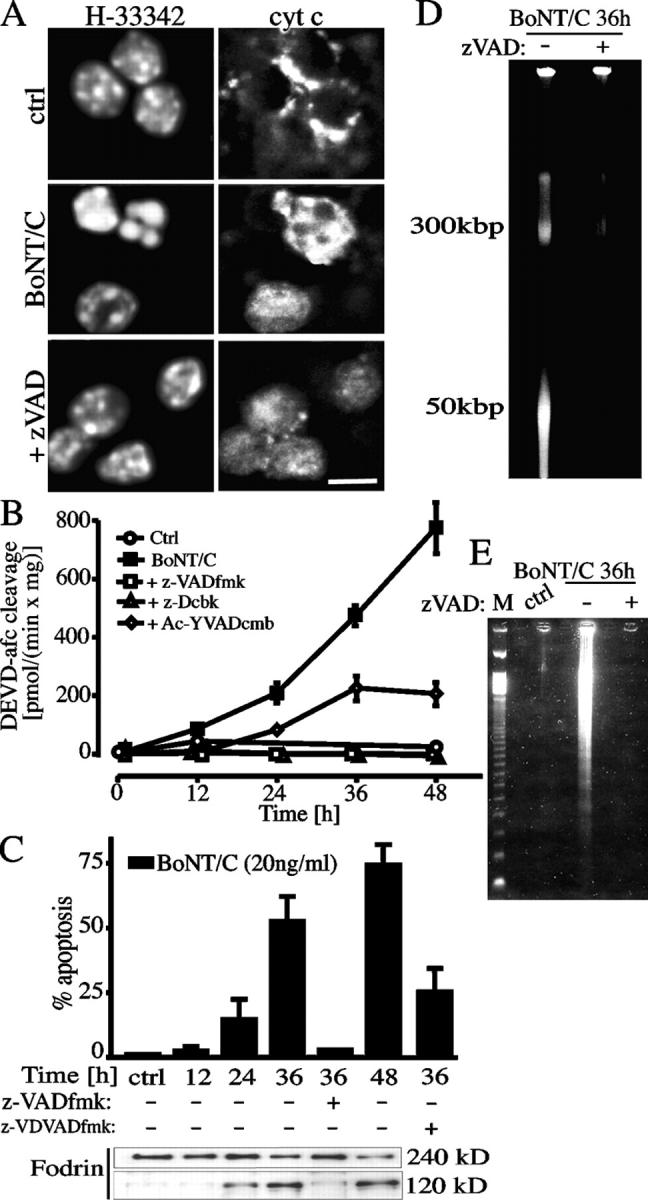
Apoptotic demise of the cell bodies is a caspase-dependent process. (A) Cytochrome c release analyzed by confocal microscopy at the level of the cell bodies in BoNT/C-treated CGCs. The release, denoted by the diffuse staining, was not prevented by caspase inhibition (e.g., by 100 μM zVAD-fmk). Cells were exposed to 20 ng/ml BoNT/C for 30 h. Shown are the time course of caspase activation measured by enzymatic assay (B) and fodrin cleavage (C) in CGC lysates exposed to 20 ng/ml BoNT/C for the indicated times. Caspase inhibition by 100 μM zVAD-fmk prevented the increase in DEVD-afc cleaving activity (B), fodrin cleavage and apoptosis (C), nuclear condensation (A), HMM DNA fragmentation (D), and DNA laddering (E). The caspase-2 inhibitor zVDVAD-fmk (1 μM) partially protected from apoptosis. Bar, 10 μm.
