Figure 1.
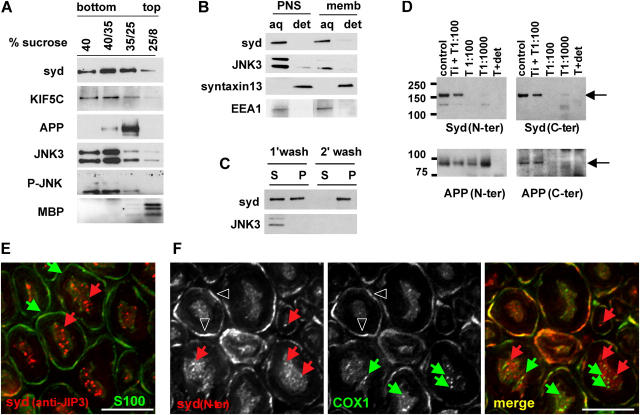
Syd is a peripheral membrane protein associated with axonal vesicular structures in mouse sciatic nerve. (A) After flotation on sucrose step gradients, syd, KIF5C, JNK3, and P-JNK are present in both the soluble fraction (40% sucrose) and the membrane fraction (35/25 interface). The 40/35 interface contains both soluble and membrane-bound proteins (note that JNK antibodies recognize the 46- and 54-kd isoforms). (B) Sciatic nerve PNS or floating membrane fractions (memb) were treated with Triton X-114 at 4°C. Syd and JNK3 are found in the aqueous phase (note that the top band recognizing the JNK3 54-kd isoform is below detection level at this exposure time in the membrane extraction). (C) After carbonate wash of sciatic nerve PNS, a significant amount of syd remains associated with membranes. (D) Brain membrane fractions were treated with trypsin (T) in the presence or absence of soybean trypsin inhibitor (Ti) or Triton X-100 (det), as indicated. APP is protected from trypsin digestion, whereas syd is not detected with NH2- or COOH-terminal antibodies after digestion. (E) Sciatic nerve cross sections were stained for syd (anti-JIP3) and S100, a Schwann cell marker. Deconvolution analysis shows punctate syd staining. Red arrows, syd puncta; green arrows, Schwann cells. (F) Sciatic nerve cross sections were stained for syd (syd N-ter) and COX1. No colocalization is observed. Red arrows, syd puncta; green arrows, COX1 puncta; arrowheads, myelin outer layer. Bars, 5 μm.