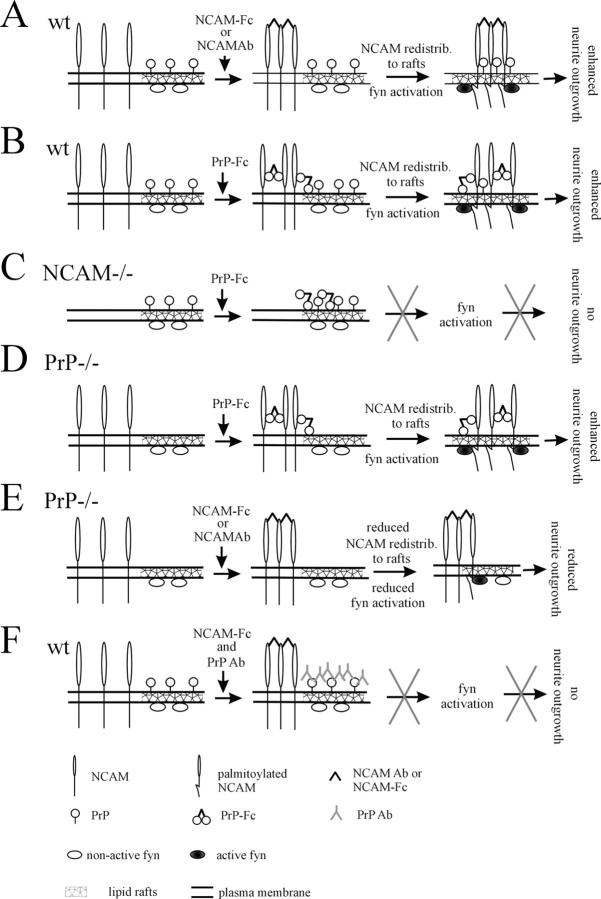
Figure 10.
Proposed model of NCAM-to-PrP interactions in NCAM/PrP-mediated neurite outgrowth. (A) In NCAM+/+ (wt) neurons, at resting conditions PrP accumulates in lipid rafts enriched in fyn. NCAM, which binds to RPTPα outside of lipid rafts (omitted for clarity) and activates fyn (Bodrikov et al., 2005), is largely excluded from lipid rafts. Application of bivalent NCAM-Fc or multivalent NCAM antibodies to neurons induces clustering of NCAM, resulting in its palmitoylation that redistributes NCAM to lipid rafts (Niethammer et al., 2002). In lipid rafts, cis interactions between NCAM and PrP further recruit and stabilize NCAM in lipid microdomains activating fyn via NCAM, and finally resulting in neurite outgrowth that is enhanced over neurite outgrowth in the absence of NCAM antibodies or NCAM-Fc. (B) Application of bivalent PrP-Fc to NCAM+/+ (wt) neurons to mimic trans interactions between NCAM at the cell surface and PrP on adjacent membranes and in the ECM of the brain also induces clustering of NCAM, favoring its redistribution to lipid rafts. Moreover, PrP-Fc may directly link NCAM to lipid-enriched microdomains due to the interactions between PrP-Fc and lipids (Walmsley et al., 2003). NCAM redistribution to lipid rafts results in fyn activation via NCAM and in enhanced neurite outgrowth. (C) In NCAM−/− neurons, application of PrP-Fc is ineffective because PrP-Fc cannot act through its neuronal receptor NCAM and thus the fyn-activating signal is lost, resulting in neurite outgrowth that is not different from neurite outgrowth in the absence of PrP. (D) Application of PrP-Fc to PrP−/− neurons induces clustering of NCAM and bridging it to lipid rafts favoring NCAM redistribution to lipid rafts, fyn activation, and neurite outgrowth (similarly to B). (E) Application of NCAM-Fc or NCAM antibodies to PrP−/− neurons induces clustering of NCAM and its redistribution to lipid rafts via palmitoylation of the NCAM intracellular domain. However, NCAM redistribution to lipid rafts in PrP−/− neurons is reduced because NCAM/PrP cis interactions stabilizing NCAM in lipid rafts are lost. This results in reduced levels of fyn activation and neurite outgrowth when compared with PrP+/+ neurons. (F) PrP antibodies applied to neurons induce clustering of PrP, but not fyn activation and neurite outgrowth induction because PrP does not have a fyn-activating signal. PrP antibodies block cis interactions between PrP and NCAM, thereby inhibiting NCAM-mediated neurite outgrowth.