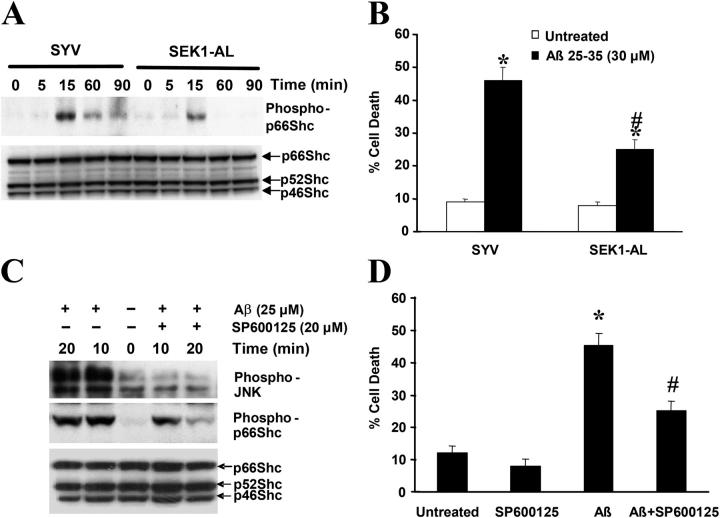
Figure 5.
Reduction of JNK activation partially blocks Aβ-induced p66Shc phosphorylation. (A) p66Shc phosphorylation at Ser36 in SH-SY5Y cells overexpressing either SYV or SEK1-AL after addition of 30 μM Aβ at various times after a 16-h serum starvation period was detected by Western blot analysis, sequentially using anti–phospho-p66Shc (Ser36) and anti-Shc antibodies. The blots are representative of three separate experiments. (B) Cells were treated with 30 μM Aβ for 24 h in serum-free media containing N2 supplements. Trypan blue exclusion was used to determine cell death. Data are means ± SEM for three separate experiments performed in duplicate. *, P < 0.05 versus untreated cells; #, P < 0.05 versus Aβ-treated SYV cells. (C) SH-SY5Y cells were serum-starved for 16 h and were either left untreated or pretreated with 20 μM SP600125 for 1 h followed by 30-μM Aβ treatment for 10 and 20 min. Cells were harvested and cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies that recognized phospho-FKHR, phospho-Shc (Ser36), and Shc. The blots are representative of three separate experiments. (D) SH-SY5Y cells were either left untreated or pretreated with 20 μM SP600125 for 1 h, and then treated with 30 μM Aβ for 24 h. Cell death was measured by Trypan blue exclusion. *, P < 0.05 versus untreated cells; #, P < 0.05 versus Aβ-treated cells.