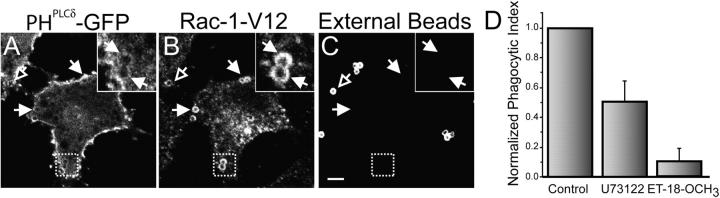
Figure 6.
Disappearance of PI(4,5)P2 from Rac1-V1–induced phagosomes. RBL-2H3 cells engineered to express stably the two constructs described in Fig. 4 were transiently transfected with PHPLCδ-GFP (A). Beads coated with anti-CD25 antibodies were then added and the cells were incubated for 60 min at 37°C, then rapidly cooled to 4°C and treated with Cy5-conjugated anti–mouse antibodies to identify beads that were accessible from the medium, i.e., not completely internalized (C). A small amount of light refracted by latex is visible in both internal and external beads. This refraction is apparent only at the center of the beads and is clearly distinguishable from the more peripheral antibody labeling. The cells were next fixed, permeabilized and immunostained with anti-myc antibodies to reveal the location of myc-Rac1-V12 (B). Open arrows point to externally accessible beads and closed arrows point to sealed phagosomes. Bar, 5 μm. Insets show a magnification of the area indicated by the square in the main panels. (D) Phagocytosis was induced in the transfected RBL-2H3 cells as described in Fig. 4. The cells were otherwise untreated, or were pretreated with the PLC inhibitors U73122 (1 μM) or ET-18-OCH3 (25 μM) for 10 min before phagocytosis. Extracellular beads were labeled and the number of beads ingested after 20 min was quantified under a fluorescence microscope. The phagocytic index was normalized to allow comparison of multiple experiments. The data are the means ± SEM of three experiments, each scoring at least 50 cells.