Figure 1.
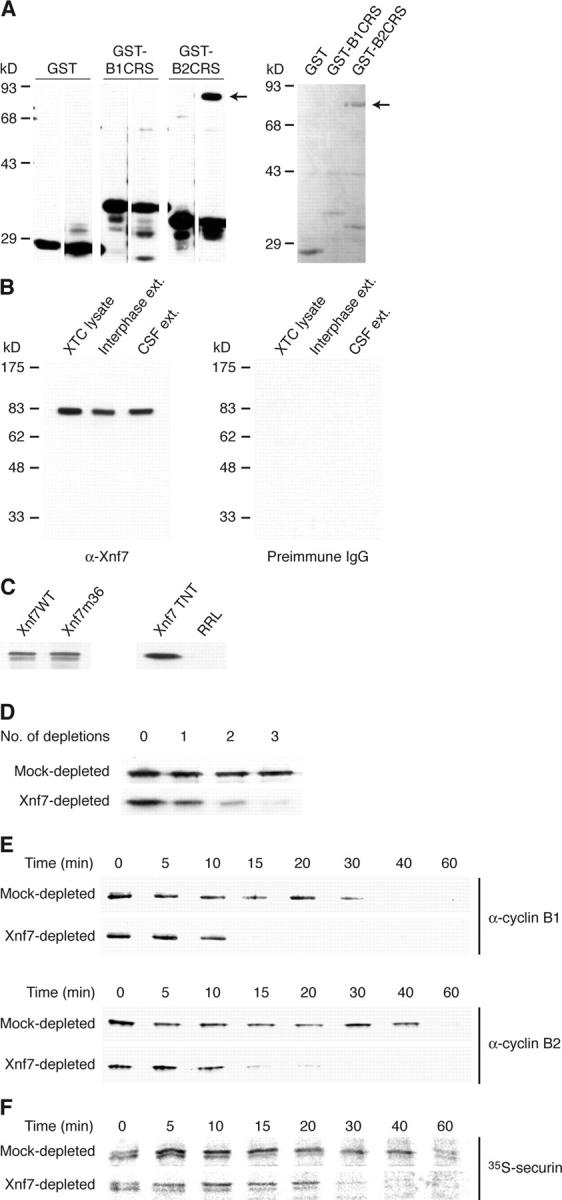
Immunodepletion of Xnf7 accelerates exit from CSF arrest. (A) Xnf7 interacts with the cyclin B2 CRS. Glutathione-Sepharose beads were coupled to GST, GST-cyclin B1 CRS, or GST-cyclin B2 CRS and incubated with egg extracts. (left) Beads were washed, and bound material was conjugated to biotin. Biotinylated material was resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with HRP-streptavidin. The left lane of each panel shows proteins present on the beads alone; the right lanes show proteins bound after incubation with extract. (right) Beads were washed and bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. The arrows indicate the ∼80-kD band that was identified by mass spectrometry as Xnf7. (B) Characterization of Xnf7 antibodies. Xenopus XTC cell lysate and interphase and CSF-arrested egg extracts were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with affinity-purified Xnf7 antibodies (left) or purified preimmune IgG (right). (C) Xnf7 wild-type (Xnf7WT) and Xnf7 mutant 36 (Xnf7m36) expressed in Escherichia coli, rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) programmed with Xnf7 (Xnf7 TNT), and unprogrammed RRL were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with affinity-purified Xnf7 antibodies. (D) Immunodepletion of Xnf7 from egg extracts. Purified anti-Xnf7 antibodies or purified preimmune IgG were coupled to protein A–Sepharose and incubated with extracts. Three consecutive depletions were performed and depleted extracts were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-Xnf7 antibodies. (E) Immunodepletion of Xnf7 accelerates the degradation of cyclin B1 and cyclin B2 during exit from CSF arrest. CSF extracts were depleted and incubated at 23°C for 30 min. CaCl2 was added to extracts, and aliquots removed at the indicated times after CaCl2 addition were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti–cyclin B1 or anti–cyclin B2 antibodies. (F) Immunodepletion of Xnf7 accelerates the degradation of securin during exit from CSF arrest. CSF extracts were depleted, supplemented with 35S-securin, and incubated at 23°C for 30 min. CaCl2 was added to extracts, and aliquots removed at the indicated times were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography.
