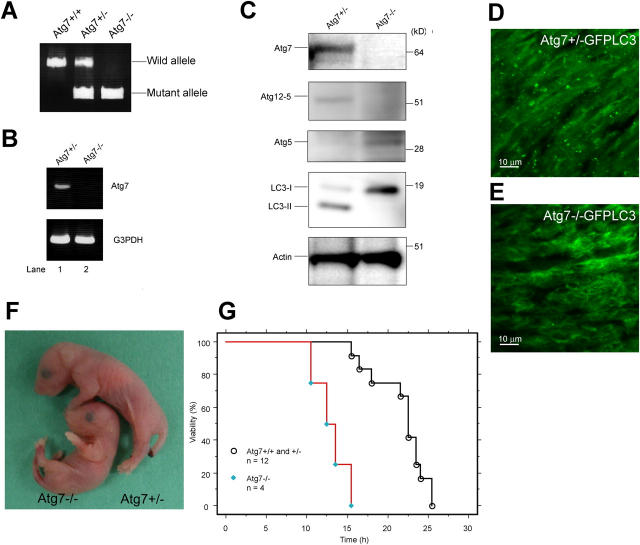
Figure 2.
The phenotypes of Atg7-deficient mice. (A) PCR analysis of genomic DNA extracted from wild-type, Atg7 +/−, and Atg7 −/− mice tail. The amplified fragments derived from wild and mutant alleles are indicated. (B) Expression of Atg7 transcript. Atg7 transcript was detected by RT-PCR analysis. The region amplified was between exons 12 and 13. G3PDH cDNA was amplified as an internal control. (C) ATG conjugation systems in Atg7 −/− mice liver. The liver homogenate was centrifuged at 800 g for 10 min and the postnuclear supernatant (PNS) was immunoblotted with antibodies against Atg7, Atg5, LC3, and actin as a loading control. The bottom panel of Atg5 blotting is the long exposure of the top panel to detect free Atg5. Data shown are representative of three separate experiments. (D and E) Deficiency of autophagosome formation in Atg7 −/− heart. Atg7 +/− (D) and Atg7 −/− (E) mice expressing GFP-LC3 were obtained by caesarean delivery and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Representative results obtained from each neonatal heart at 3 h after caesarean delivery. (F) Morphology of Atg7 +/− and Atg7 −/− mice. (G) Kaplan-Meier curves of survival of newborn mice. Control and Atg7 −/− mice were delivered by caesarean section, and their survival was followed up to 26 h.