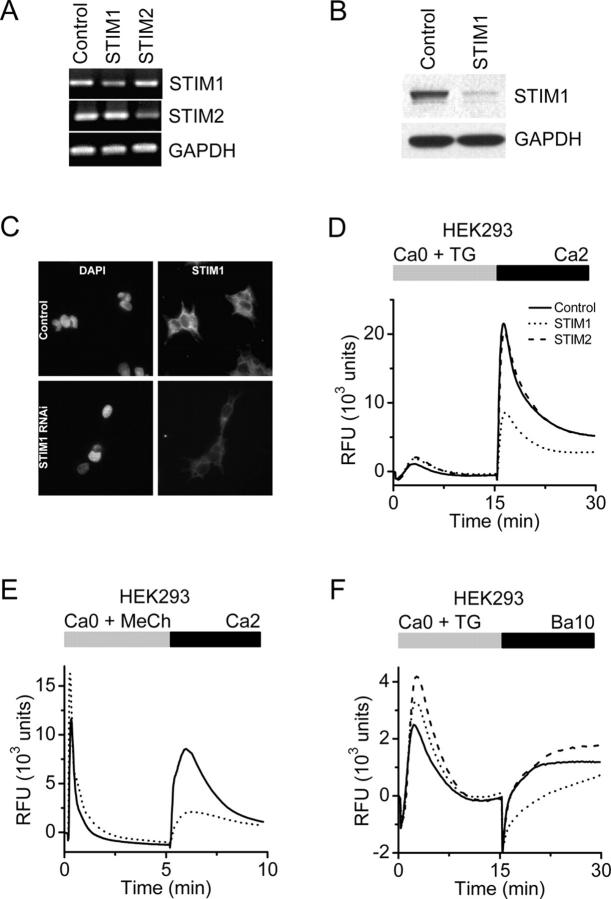
Figure 6.
Suppression of STIM1 in HEK293 cells inhibits SOC influx. (A) RT-PCR analysis. STIM1 and STIM2 mRNA levels were reduced in cells transfected with the appropriate siRNA to <50% of control cells (transfected with scrambled siRNA). GAPDH levels were unchanged in either treatment group. (B) Western blot analysis. In cells transfected with the STIM1 siRNA, STIM1 protein levels were reduced to <10% of control levels, whereas GAPDH levels were unchanged. (C) Immunofluorescence localization of STIM1 in HEK293 cells. Nuclear staining pattern (left) with DAPI (Molecular Probes) in HEK293 cells treated with either a scrambled siRNA (top) or siRNA to STIM1 (bottom). No change in nuclear staining pattern or intensity was observed after RNAi-induced suppression of STIM1. STIM1-associated immunofluorescence (right) in HEK293 cells treated with either control (top) or STIM1 (bottom) siRNAs. In control cells, STIM1 has a diffuse reticulated localization pattern with some punctuate staining, which is consistent with expression associated with plasma membrane and ER. The intensity of STIM1 immunofluorescence was markedly decreased in the cells treated with STIM1 siRNA. (D) Calcium signals in HEK293 cells after RNAi-mediated knockdown. Suppression of STIM1 (dotted line) reduced SOC influx by 60% compared with control (solid line; P < 10−4, unpaired t test), whereas suppression of STIM2 (dashed line) had little effect. Data indicate RFUs in 384-well plates monitored in a FLIPR384 fluorimeter. The traces are from a representative experiment, and are averaged signals from 48 wells per group. Traces from cells treated with vehicle (DMSO) instead of TG were essentially flat (not depicted for clarity). (E) Calcium signals after muscarinic receptor activation. RT-PCR analysis revealed that the muscarinic receptor, subtype m3, is expressed in our HEK293 cells (not depicted). 300 μM of methylcholine evoked Ca2+-release transients in Ca2+-free buffer were not inhibited by STIM1 suppression, but SOC influx upon readdition of 2 mM Ca2+ was greatly reduced in STIM1 siRNA-treated cells (dotted line) compared with control cells (solid line). The apparent enhancement of the methylcholine-evoked Ca2+ release transient in the STIM1-suppressed cells was not a consistent finding. (F) TG-induced Ba2+ entry. The rate of TG-induced Ba2+ entry in STIM1-suppressed cells (dotted line) was significantly lower than in control cells (solid line) or STIM2-suppressed cells (dashed line; P < 10−4, unpaired t test).