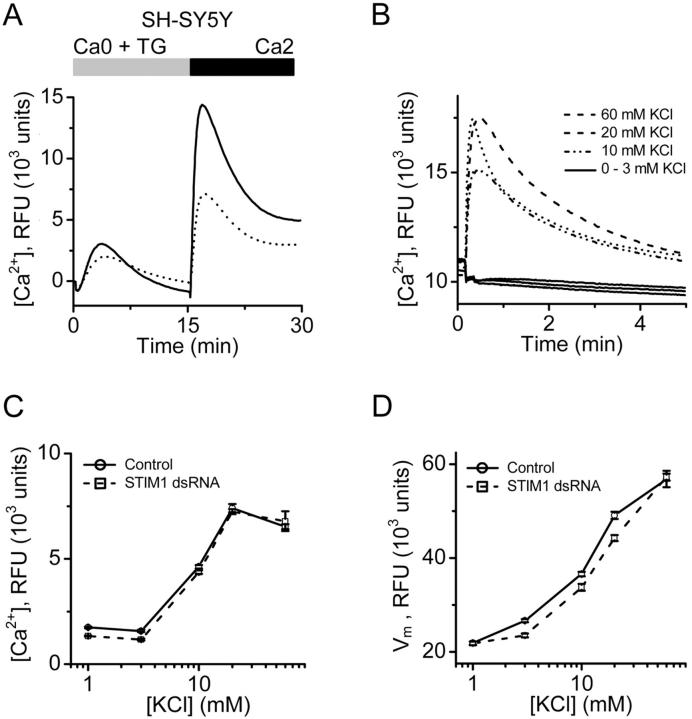
Figure 8.
Specificity of STIM1 RNAi in SH-SY5Y cells. (A) Effects of STIM1 RNAi on SOC influx in SH-SY5Y cells. TG-dependent Ca2+ entry in STIM1 siRNA-treated cells (dotted line) is greatly reduced compared with control cells (solid line). Traces from cells treated with vehicle (DMSO) instead of TG were essentially flat (not depicted for clarity). (B) KCl-evoked Ca2+ signals as a measure of voltage-gated Ca2+ channel activity. Data presented as fluo-4 RFUs. At concentrations of 3 mM KCl or below, no significant change in cytosolic Ca2+ was observed. At 10, 20, and 60 mM KCl, a rapid rise in cytosolic Ca2+ was detected. (C) Maximal KCl-evoked RFU values are not different in control and STIM1-knockdown cells. (D) STIM1 suppression does not affect the resting membrane potential or the response to depolarization in SH-SY5Y cells. To monitor changes in membrane potential, a FLIPR membrane potential assay kit (Molecular Devices) was used as per the manufacturer's protocols. Data presented in RFUs. Cells were depolarized with increasing concentration of KCl, as in B. Error bars represent SD.