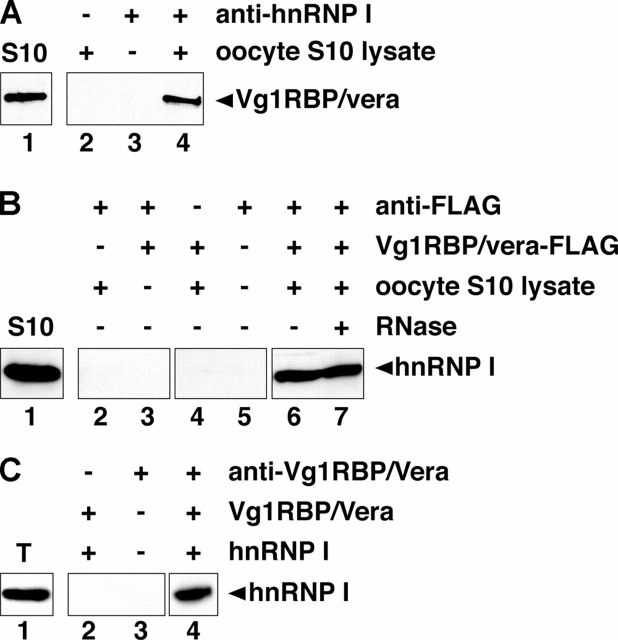
Figure 3.
Vg1RBP/vera and hnRNP I interact in vitro and in vivo. (A) Anti-hnRNP I was used to immunoprecipitate endogenous hnRNP I from oocyte S10 lysate. Bound Vg1RBP/vera was detected by immunoblotting (lane 4). Shown in lane 1 is the total Vg1RBP/vera in the lysate, and immunoprecipitation with protein G beads with or without lysate is shown in lanes 2 and 3, respectively. (B) In vitro–translated Vg1RBP/vera-FLAG was incubated with oocyte S10 lysate. Immunoprecipitations were performed using anti-FLAG beads with S10 lysate (lane 2), anti-FLAG beads with in vitro–translated Vg1RBP/vera-FLAG (lane 3), Sepharose beads with S10 lysate plus in vitro–translated Vg1RBP/vera-FLAG (lane 4), anti-FLAG beads alone (lane 5), and anti-FLAG beads with S10 lysate plus in vitro–translated Vg1RBP/vera-FLAG in the absence (lane 6) or presence (lane 7) of RNase A. Total (lane 1) and bound (lanes 2–7) proteins were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-hnRNP I. (C) Recombinant Vg1RBP/vera and hnRNP I were translated in vitro and mixed; shown in lane 1 is the input amount of in vitro–translated hnRNP I. Immunoprecipitation reactions were performed using protein G beads in the presence of recombinant Vg1RBP/vera and hnRNP I (lane 2) and anti-Vg1RBP/vera bound to protein G beads either alone (lane 3) or with recombinant Vg1RBP/vera and hnRNP I (lane 4). Total (lane 1) and bound (lanes 2–4) proteins were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and were immunoblotted with anti-hnRNP I. For each panel (A–C), samples were run on the same gel, but lane order was changed for presentation in the figure; adjacent lanes are boxed.