Figure 2.
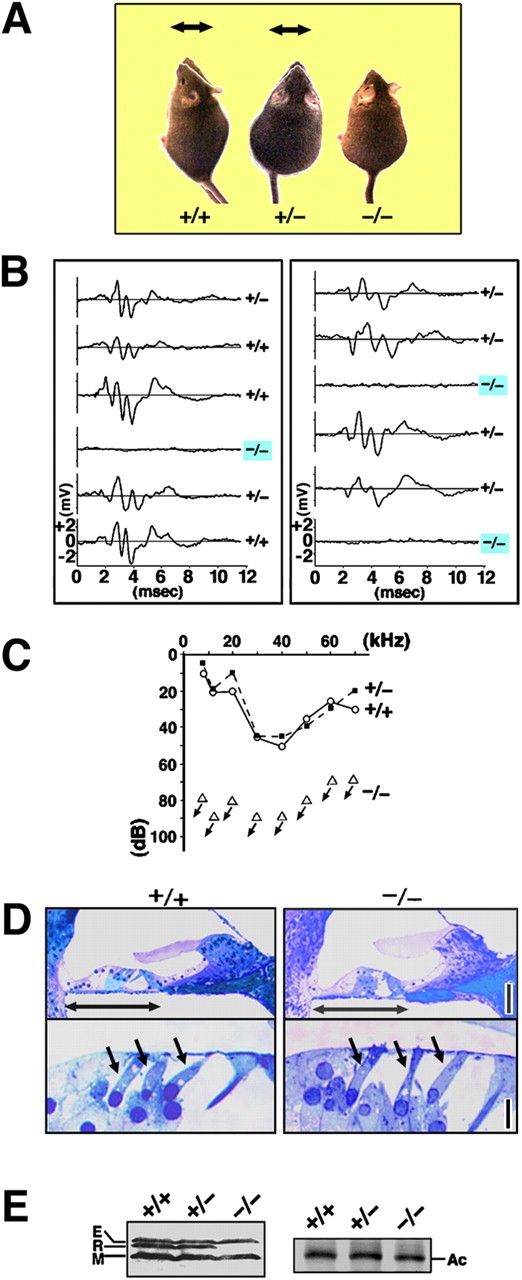
Deafness of Rdx −/− mice. (A) Loss of Preyer's reflex in Rdx −/− mice. Time-lapse photography captures Preyer's reflex in Rdx +/+ and Rdx +/− mice, head movements (arrows), but not in Rdx −/− mice. Two successive frames after a loud handclap (1-s interval) were superimposed. These 10-wk-old mice show similar growth rates. (B) ABR to stimuli of 70-dB SPL (20 kHz) in two sets of Rdx +/− intercross littermates (left, 5-wk-old; right 10-wk-old). Among 12 littermates in total, three show no ABR, and were afterwards genotyped as Rdx −/− mice (blue squares). (C) Hearing thresholds of 10-wk-old Rdx +/+, Rdx +/−, and Rdx −/− mice at various sound frequencies. Rdx +/+ and Rdx +/− mice show normal hearing thresholds (10–50 dB SPL), whereas Rdx −/− mice show profound deafness (hearing threshold, >70–90 dB SPL). (D) Toluidine blue–stained Epon semi-thin sections of the cochlea. No gross morphological difference is observed in the organ of Corti (double-headed arrows) including hair cells (single-headed arrows) between Rdx +/+ and Rdx −/− mice. Bars, 50 μm (top panels); 10 μm (bottom panels). (E) Western blot analysis of isolated cochleae of the Rdx +/+ , Rdx +/−, and Rdx −/− mice with anti-ERM pAb (TK89) that recognizes ezrin (E), radixin (R), and moesin (M) equally. In the Rdx −/− cochlea, radixin becomes undetectable without significant up-regulation of ezrin or moesin. Silver-stained bands of actin (Ac) in the same gels are present to show that an equal amount of cell lysate was applied in each lane.
