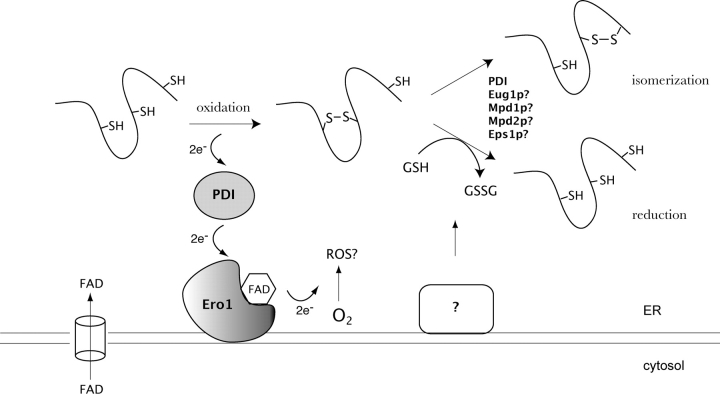
Figure 1.
Schematic model of oxidative protein folding in the yeast ER. The formation of disulfide bonds in the ER is driven by Ero1p. FAD-bound Ero1p oxidizes PDI, which then subsequently oxidizes folding proteins directly. FAD-bound Ero1p then passes electrons to molecular oxygen, perhaps resulting in the production of ROS. FAD, which is synthesized in the cytosol, can readily enter the ER lumen and stimulate the activity of Ero1p. Disulfide isomerization and reduction may be performed by some of the four homologues of PDI, Eug1p, Mpd1p, Mpd2p, or Eps1p, in addition to PDI itself. Reduced glutathione (GSH) may also assist in disulfide reduction, resulting in the production of oxidized glutathione (GSSG).